|
|
|
Asthma attacks and symptoms usually get started by specific triggers (such as viruses, allergies, gases, and air particles). You should talk to your doctor about these triggers and find ways to avoid or get rid of them.
Colchicine is a highly poisonous alkaloid originally extracted from a type of saffron plant that is used mainly to treat gout.
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
There can actually be a 25-hour time difference between certain locations in the world. The International Date Line passes between the islands of Samoa and American Samoa. It is not a straight line, but "zig-zags" around various island chains. Therefore, Samoa and nearby islands have one date, while American Samoa and nearby islands are one day behind. Daylight saving time is used in some islands, but not in others—further shifting the hours out of sync with natural time.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
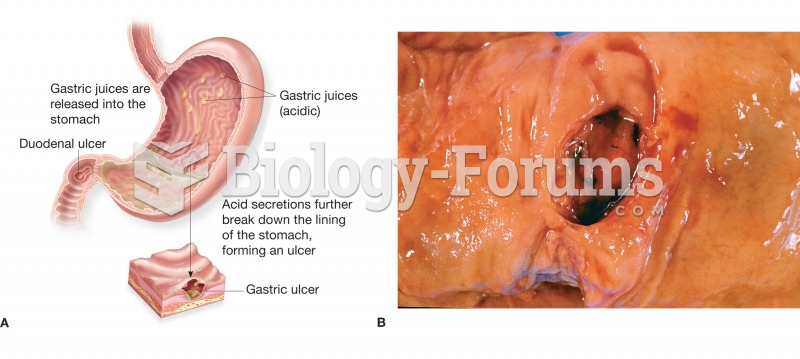 (A) Figure illustrating the location and appearance of a peptic ulcer in both the stomach and the du
(A) Figure illustrating the location and appearance of a peptic ulcer in both the stomach and the du
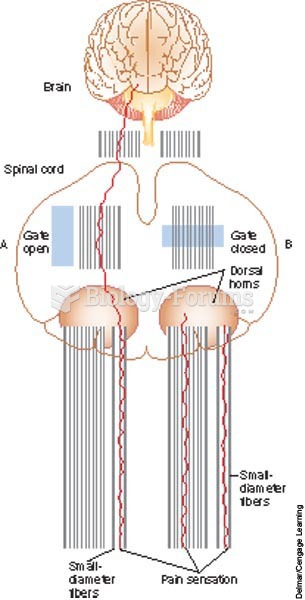 Gate Control Theory, Gate control, Open gate, Closed gate, Pain, Nerve transmission of pain, Pain ma
Gate Control Theory, Gate control, Open gate, Closed gate, Pain, Nerve transmission of pain, Pain ma