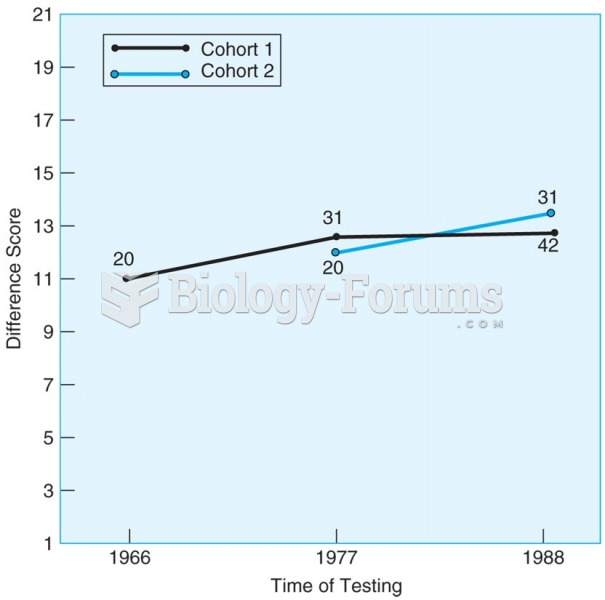
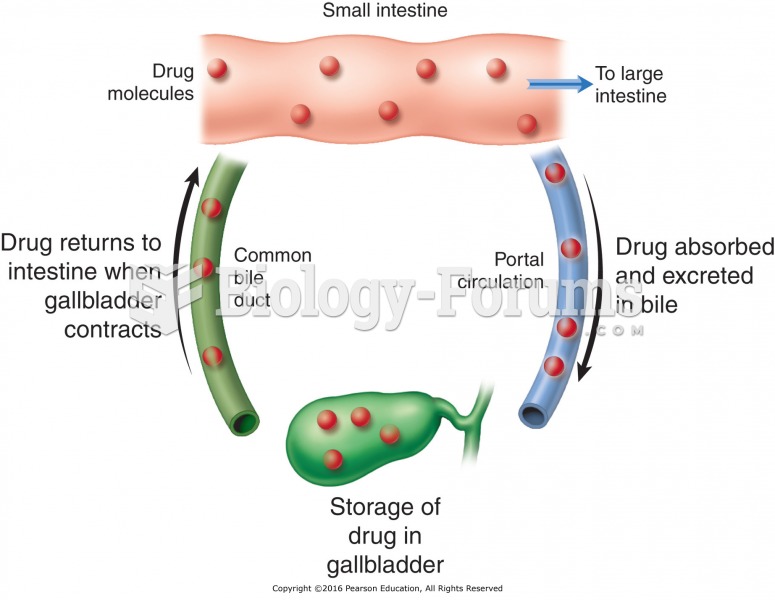
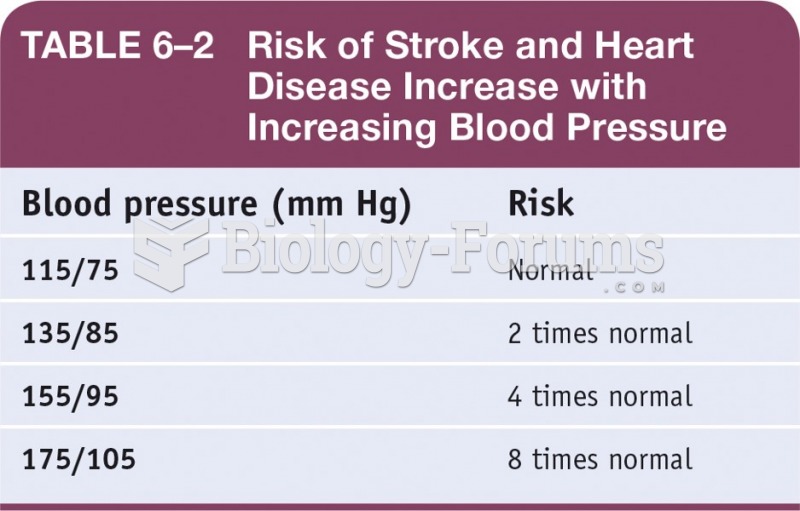
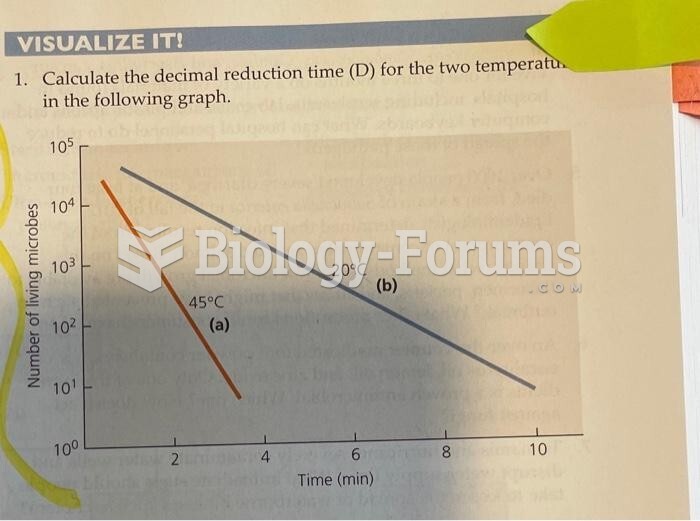
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The horizontal fraction bar was introduced by the Arabs.
Did you know?
Thyroid conditions may make getting pregnant impossible.
Did you know?
More than one-third of adult Americans are obese. Diseases that kill the largest number of people annually, such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, stroke, and hypertension, can be attributed to diet.
Did you know?
There are more sensory neurons in the tongue than in any other part of the body.
Did you know?
Oxytocin is recommended only for pregnancies that have a medical reason for inducing labor (such as eclampsia) and is not recommended for elective procedures or for making the birthing process more convenient.