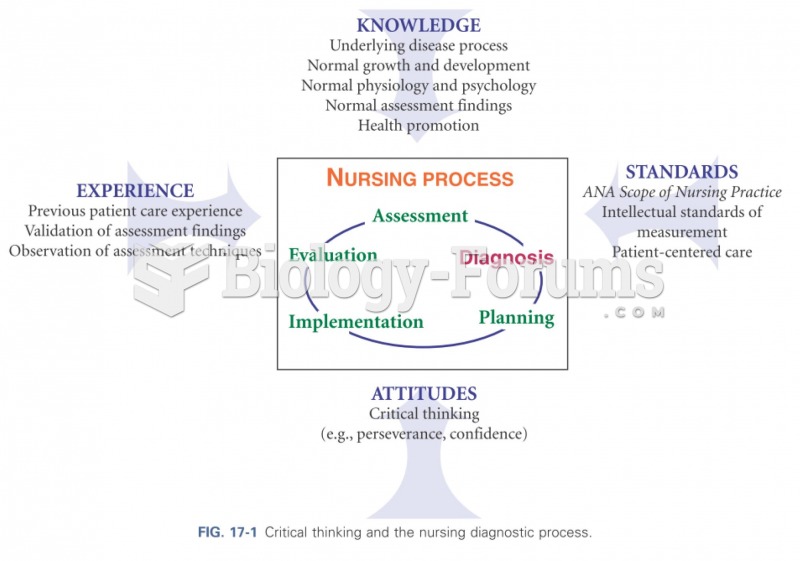
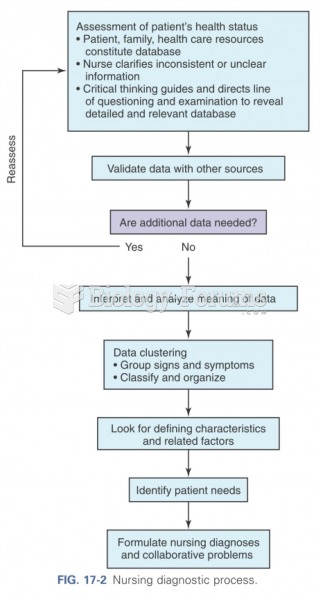
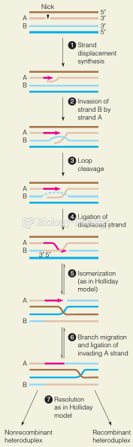
|
|
|
Did you know?
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Did you know?
Women are 50% to 75% more likely than men to experience an adverse drug reaction.
Did you know?
Approximately 500,000 babies are born each year in the United States to teenage mothers.
Did you know?
The strongest synthetic topical retinoid drug available, tazarotene, is used to treat sun-damaged skin, acne, and psoriasis.
Did you know?
More than 2,500 barbiturates have been synthesized. At the height of their popularity, about 50 were marketed for human use.