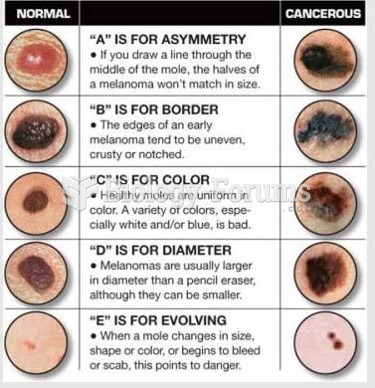
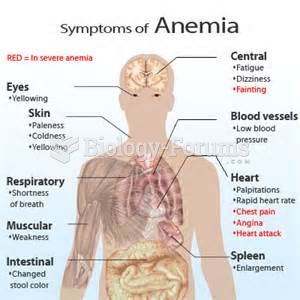
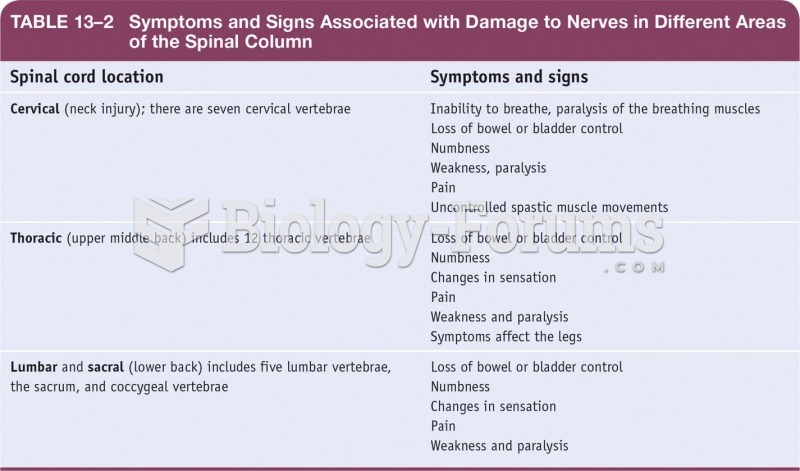
Answer to Question 1
Prostate cancer is difficult to detect and control because the causes are not known. Death rates can be lowered through early detection and awareness of the warning signals. Detection is done by a digital rectal exam of the gland and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test once a year after the age of 50. Possible warning signals include difficulties in urination (especially at night), painful urination, blood in the urine, and constant pain in the lower back or hip area.
Factors that may decrease the risk include increasing the consumption of tomato-rich foods and fatty fish in the diet two or three times per week, avoiding a high-fat (especially animal fat) diet, increasing daily consumption of produce and grains, and maintaining recommended vitamin D intake (obtained through supplements, multivitamins, and fortified milk and manufactured by the body when exposed to sunlight). Vigorous exercise such as jogging or swimming has been shown to lower risk of advanced prostate cancer by as much as 70 percent in older men, and even brisk walking has been shown to halt the cancer's progression.
Answer to Question 2
For most of the 20th century, a person's genetic traits were thought to be unalterable. Once a person inherited risk of disease, it was believed that there was little that could be done to change that risk. The field of epigenetics has drastically disrupted our understanding of genetics and has shown that environmental choices change the way our genes work and that certain genes can be turned off and on by lifestyle choices. This happens on the molecular level through one of two processes.
Chemical tags called methyl groups can be added directly to DNA to switch genes off. Meanwhile other chemical tags can be added to the proteins (called histones) around which DNA wraps itself, like spool on a thread. These tags then turn genes off-by coiling the bundle of protein and DNA tightly away so they cannot be reached for transcription-or turn genes on by unfurling DNA for open transcription.
These tags are added or removed depending on lifestyle choices. Whether the gene is available to be expressed depends on these tags sitting on top of the gene. The word epigenetics means on top of genetics. A person's genome has been compared to computer hardware, while the epigenome has been compared to computer software, telling the genome how to work.
Epigenetic processes can encourage tumor-friendly changes that do not involve a mutation, or they can help deter tumor development. Epigenetics is already used in some cancer treatments that silence certain genes and reactivate others.
Perhaps even more ground-breaking, researchers have discovered that epigenetic changes acquired by the environment can be passed down from parent to offspring. While these changes are reversible, they can be detected in offspring two or three generations later. For example, traumatic experiences in one generation may produce fearful associations in offspring. Food choices, in particular, affect our epigenetic code. You may be answering for food choices your grandparents made. Equally, your grandchildren may someday answer for the food choices you make.