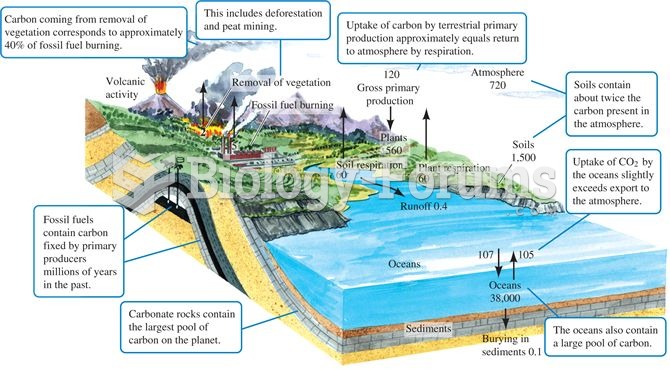
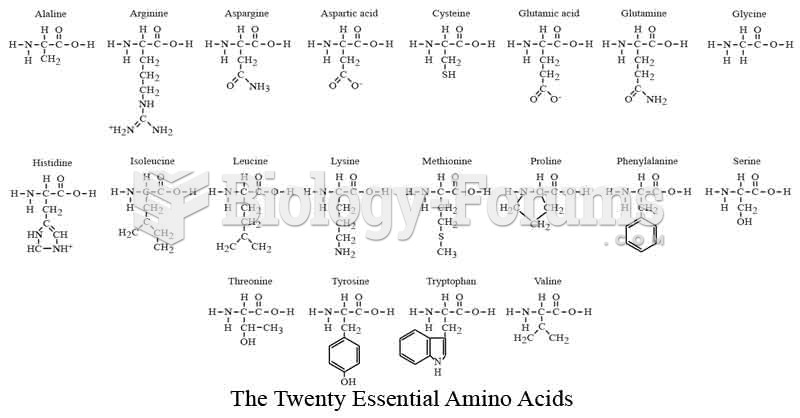
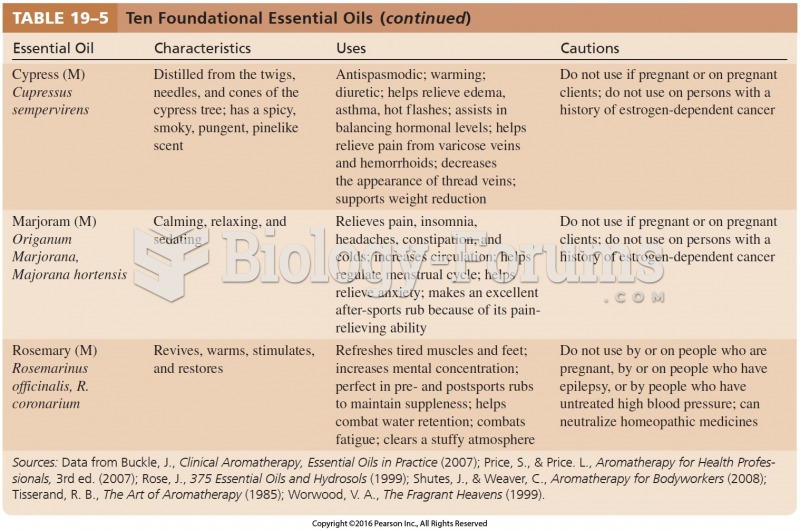
Answer to Question 1
Essential fat is found within tissues such as the muscles, nerve cells, bone marrow, intestines, heart, liver, and lungs. This type of fat is needed for normal physiological function. Without it, human health and physical performance deteriorate. Essential fat constitutes about 3 percent of the total weight in men and 12 percent in women. The percentage is higher in women because it includes sex-specific fat, such as that found in the breast tissue, the uterus, and other sex-related fat deposits.
Storage fat is the fat stored in adipose tissue, mostly just beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat) and around major organs in the body (intra-abdominal or visceral fat). This fat serves three basic functions: 1) as an insulator to retain body heat, 2) as an energy substrate for metabolism, and 3) as padding against physical trauma to the body. The amount of storage fat does not differ between men and women, except that men tend to store fat around the waist and women around the hips and thighs.
Answer to Question 2
Until the coming of dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), hydrostatic weighing was the most common technique used in determining body composition in exercise physiology laboratories. The technique centered on comparing a person's regular weight with a weight taken underwater. Because fat is more buoyant than lean tissue, comparing the two weights could determine a person's percent of fat. In addition to requiring a considerable amount of time, skill, space, equipment and a well-trained technician, this technique has several drawbacks:
First, because each individual assessment can take as long as 30 minutes, hydrostatic weighing is not feasible when testing a lot of people.
Second, the person's residual lung volume (amount of air left in the lungs following complete forceful exhalation) should be measured before testing. If residual volume cannot be measured, as is the case in some laboratories and health/fitness centers, it is estimated using the predicting equationswhich may decrease the accuracy of hydrostatic weighing.
Third, the requirement of being completely underwater made hydrostatic weighing difficult to administer to aquaphobic people. For accurate results, the individual must be able to perform the test properly.
Fourth, forcing all of the air out of the lungs (then leaning forward in a chair to be completely submerged for 5 to 10 seconds without the chair moving) is not easy for everyone but is important in obtaining an accurate reading. Leaving additional air (beyond residual volume) in the lungs makes a person more buoyant. Because fat is less dense than water, overweight individuals weigh less in water. Additional air in the lungs makes a person lighter in water, yielding a false, higher body fat percentage.