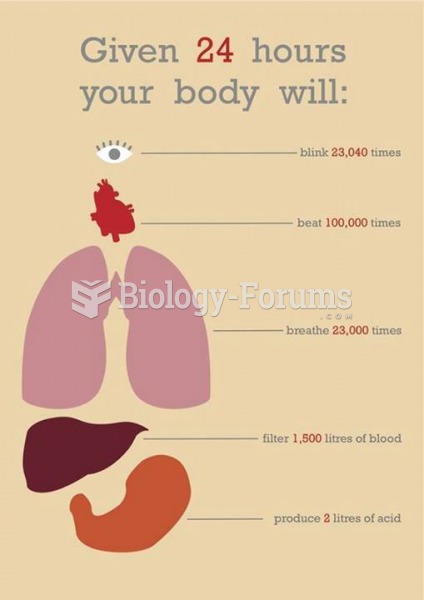
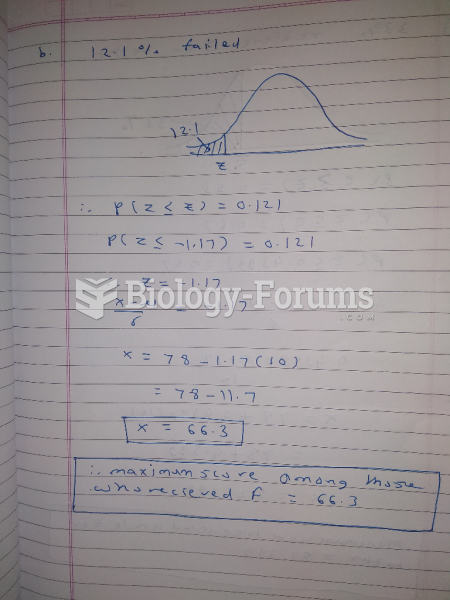
|
|
|
Signs and symptoms that may signify an eye tumor include general blurred vision, bulging eye(s), double vision, a sensation of a foreign body in the eye(s), iris defects, limited ability to move the eyelid(s), limited ability to move the eye(s), pain or discomfort in or around the eyes or eyelids, red or pink eyes, white or cloud spots on the eye(s), colored spots on the eyelid(s), swelling around the eyes, swollen eyelid(s), and general vision loss.
Everyone has one nostril that is larger than the other.
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
Human neurons are so small that they require a microscope in order to be seen. However, some neurons can be up to 3 feet long, such as those that extend from the spinal cord to the toes.
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.