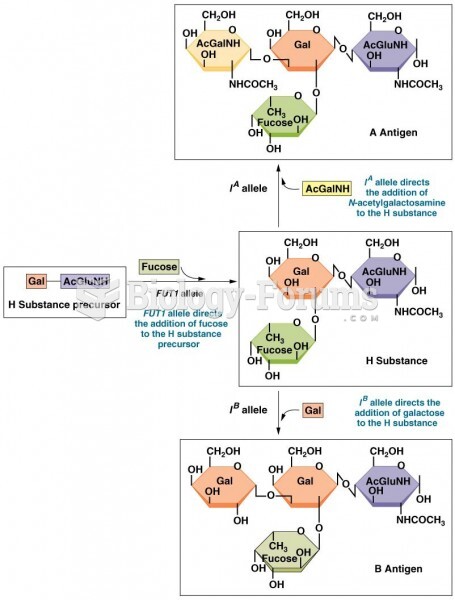
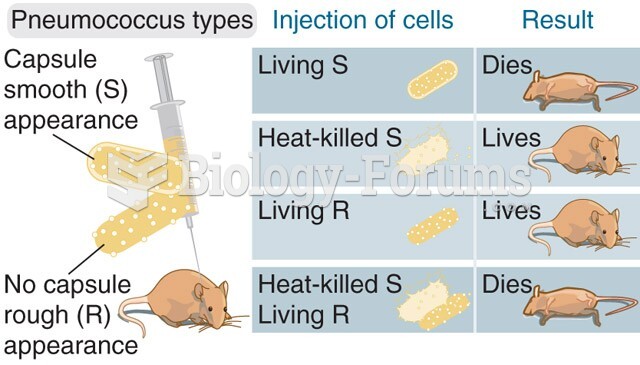
|
|
|
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
A serious new warning has been established for pregnant women against taking ACE inhibitors during pregnancy. In the study, the risk of major birth defects in children whose mothers took ACE inhibitors during the first trimester was nearly three times higher than in children whose mothers didn't take ACE inhibitors. Physicians can prescribe alternative medications for pregnant women who have symptoms of high blood pressure.
Adult head lice are gray, about ? inch long, and often have a tiny dot on their backs. A female can lay between 50 and 150 eggs within the several weeks that she is alive. They feed on human blood.
Addicts to opiates often avoid treatment because they are afraid of withdrawal. Though unpleasant, with proper management, withdrawal is rarely fatal and passes relatively quickly.
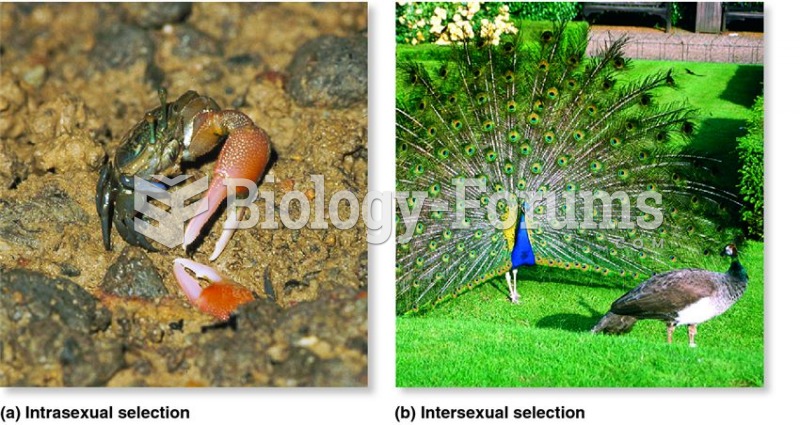



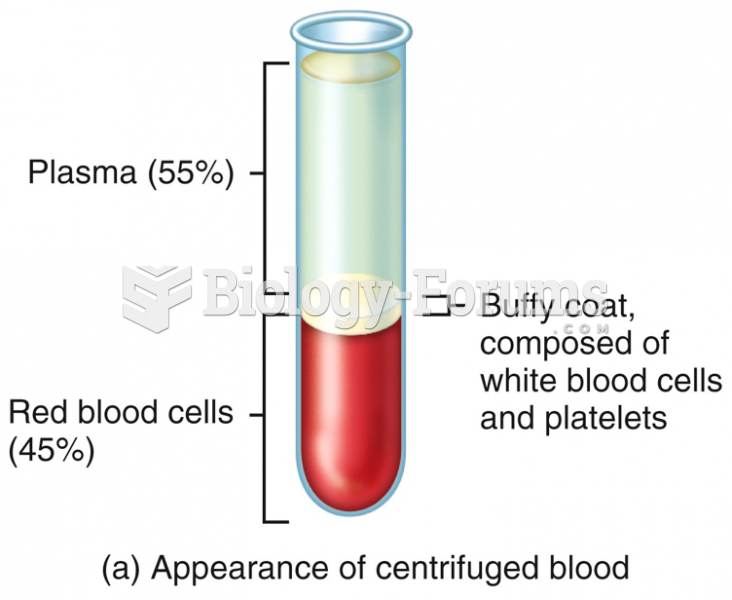
![Given the values of sin θ, determine the values of θ over the interval [0, 2pi]](https://biology-forums.com/gallery/42/medium_6_04_01_21_12_54_15.png)