Answer to Question 1
Lipids perform many tasks in the body, but most importantly they provide energy. A constant flow of energy is so vital to life that, in a pinch, any other function is sacrificed to maintain it. One safeguard against such an emergency is the store of glycogen in the liver that provides glucose to the blood whenever the supply runs short. The body's stores of glycogen are limited, however. In contrast, the body's capacity to store fat for energy is virtually unlimited due to the fat-storing cells of the adipose tissue. The fat cells of the adipose tissue readily take up and store fat, growing in size as they do so. Fat cells are more than just storage depots, however; fat cells secrete hormones that help to regulate the appetite and influence other body functions.
The fat stored in fat cells supplies 60 percent of the body's ongoing energy needs during rest. The fat embedded in muscle tissue shares with muscle glycogen the task of providing energy when the muscles are active. During some types of physical activity or prolonged periods of food deprivation, fat stores may make an even greater energy contribution. The brain and nerves, however, need their energy as glucose, and fat is an inefficient source of glucose. After a long period of glucose deprivation (during fasting or starvation), brain and nerve cells develop the ability to derive about half of their energy from a special form of fat known as ketones, but they still require glucose as well. This means that people wanting to lose weight need to eat a certain minimum amount of carbohydrate to meet their energy needs, even when they are limiting their food intakes.
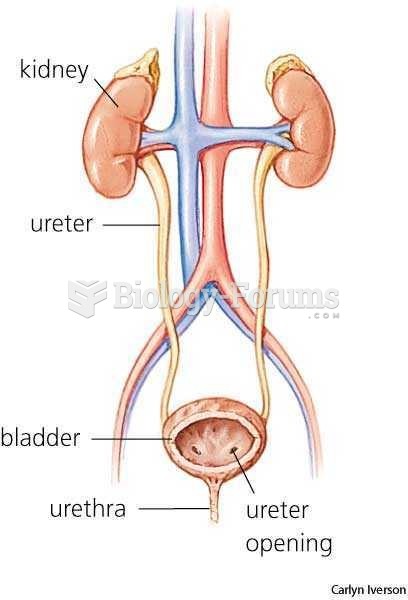
In addition to supplying energy, fat serves other roles in the body. Natural oils in the skin provide a radiant complexion; in the scalp, they help nourish the hair and make it glossy. The layer of fat beneath the skin insulates the body from extremes of temperature. A pad of hard fat beneath each kidney protects it from being jarred and damaged, even during a motorcycle ride on a bumpy road. The soft fat in a woman's breasts protects her mammary glands from heat and cold and cushions them against shock. The phospholipids and the sterol cholesterol are cell membrane constituents that help maintain the structure and health of all cells.
Answer to Question 2
b