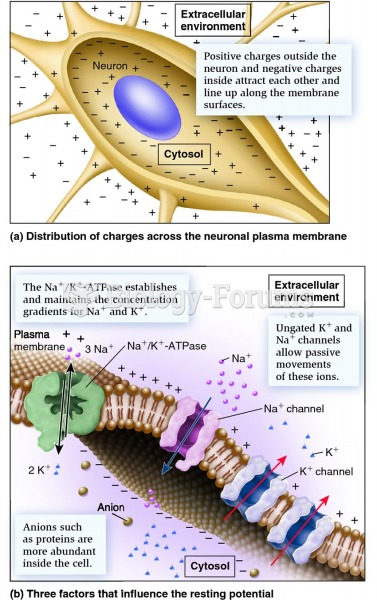
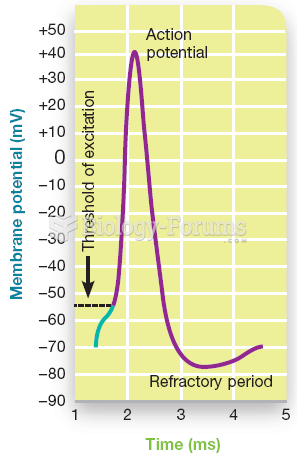
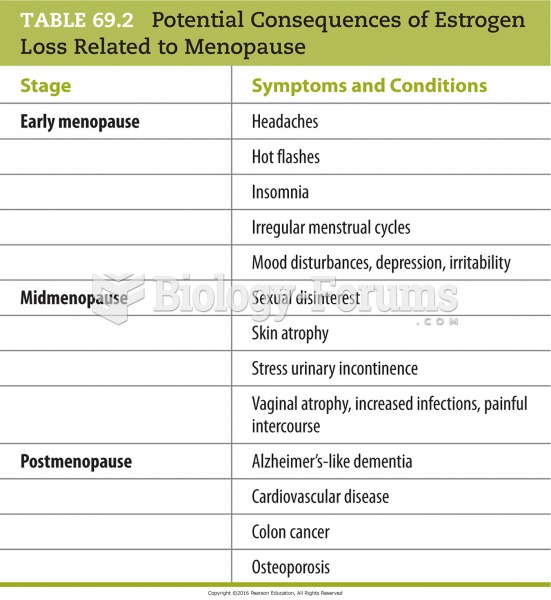
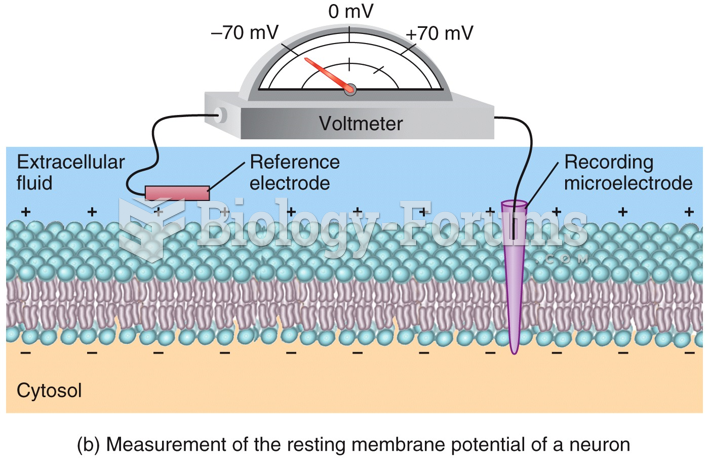
Answer to Question 1
Olestra (formerly called sucrose polyester) is a nonnutritive artificial fat made from sucrose and fatty acids. Olestra is a fat replacer, used to reduce the fat calories in processed foods. It is used to make some low-fat versions of snack foods, such as potato chips. Digestive enzymes cannot break its chemical bonds, so Olestra cannot be absorbed. Olestra binds fat-soluble vitamins and phytochemicals, causing their excretion; to partly prevent these losses, manufacturers saturate Olestra with vitamins A, D, E, and K. Large doses can cause digestive distress, but no serious problems are known to have occurred with normal use.
Answer to Question 2
Foods such as some raw produce grow close to the ground, making bacterial contamination from the soil, animal waste runoff, and manure fertilizers likely. Other kinds of produce have been responsible for transmitting dangerous foodborne illnesses to consumers. Such problems often spring from sanitation mistakes made by growers and producers. Washing produce at home to remove dirt and debris is important; however, washing may be ineffective for removing certain bacterial strains. These strainsE. coli, among othersexude a sticky, protective coating that glues microbes to each other and to food surfaces, forming a biofilm that can survive home rinsing or even industrial washing. Somewhat more effective is vigorous scrubbing with a vegetable brush to dislodge bacteria; rinsing with vinegar, which may help cut through biofilm; and removing and discarding the outer leaves from heads of leafy vegetables, such as cabbage and lettuce, before washing. Vinegar doesn't sterilize foods, but it can reduce bacterial populations, and it's safe to consume.