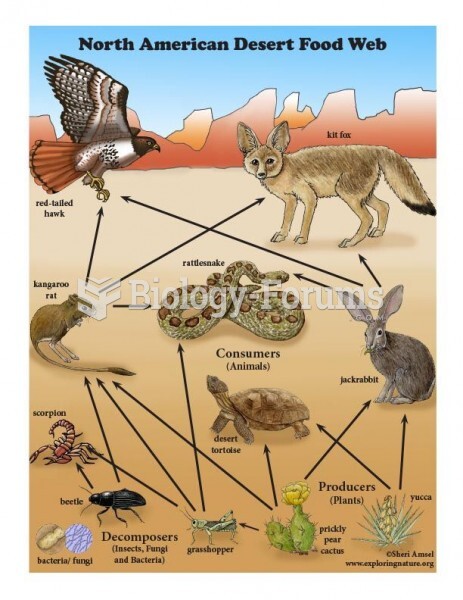
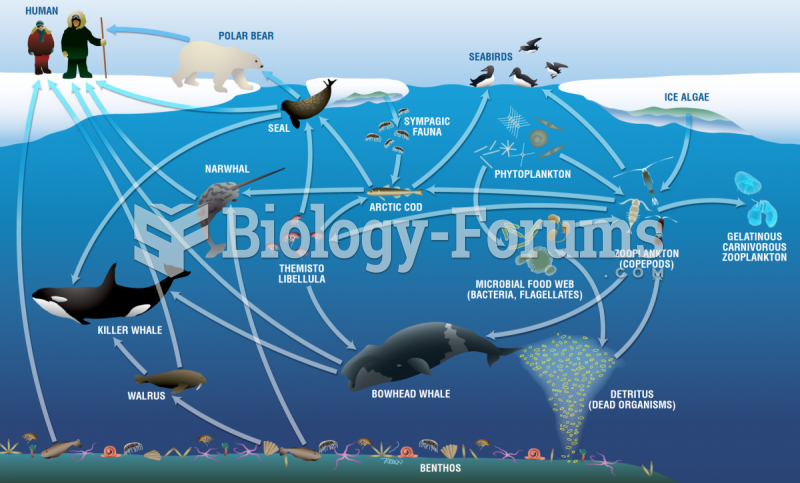
Answer to Question 1
Food neophobia is a disordered eating pattern characterized by an irrational fear or avoidance of trying new foods. Individuals with food neophobia typically eat very limited ranges of foods and often adhere to well-defined and unusual food rituals and practices. For example, an individual with food neophobia may refuse to eat foods made from two or more food items. A person may enjoy certain foods when eaten separately but may find them disgusting when joined together. In adults, these types of behaviors can be socially restricting and embarrassing. In extreme cases, they can lead to nutritional inadequacies, although some individuals with food neophobia take supplements to compensate for their poor eating habits. People with food neophobia tend to be slightly overweight because they often limit themselves to comfort foods that are high in calories, such as hamburgers, French fries, and macaroni and cheese. Perhaps surprisingly, most adults with food neophobia are not interested in therapy or other treatments.
Answer to Question 2
It is logical that brain chemistry and other biological and genetic factors might play a role in the development of an eating disorder because certain personality traits and eating behaviors are determined in part by the nervous and endocrine systems. It is also possible, however, that disordered eating may actually disrupt normal neuroendocrine function. For example, studies show that individuals with eating disorders are often clinically depressed. It is difficult to determine whether clinical depression leads to eating disorders or vice versa (or if another factor is at play). In any case, because medication used to treat clinical depression is often effective in the treatment of certain eating disorders, depression is likely a contributing factor.Scientists are working to identify genes that might influence susceptibility to eating disorders. Studies of identical and fraternal twins have provided evidence suggesting that susceptibility to eating disorders may, in part, be inherited. Although such studies cannot completely differentiate the contribution of genetics from that of environment, some research suggests that the contribution of genetics may actually be greater than that of the environment. How this occurs remains unclear, however.