|
|
|
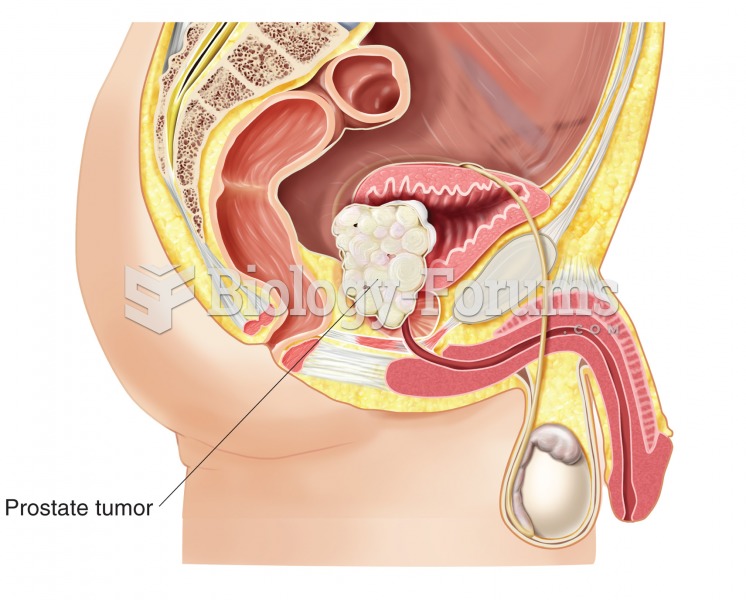
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. About 10% of Americans older than age 40 years have diverticulosis, which, when the pouches become infected or inflamed, is called diverticulitis. The main cause of diverticular disease is a low-fiber diet.
Throughout history, plants containing cardiac steroids have been used as heart drugs and as poisons (e.g., in arrows used in combat), emetics, and diuretics.
Atropine, along with scopolamine and hyoscyamine, is found in the Datura stramonium plant, which gives hallucinogenic effects and is also known as locoweed.
The most common treatment options for addiction include psychotherapy, support groups, and individual counseling.
Opium has influenced much of the world's most popular literature. The following authors were all opium users, of varying degrees: Lewis Carroll, Charles, Dickens, Arthur Conan Doyle, and Oscar Wilde.