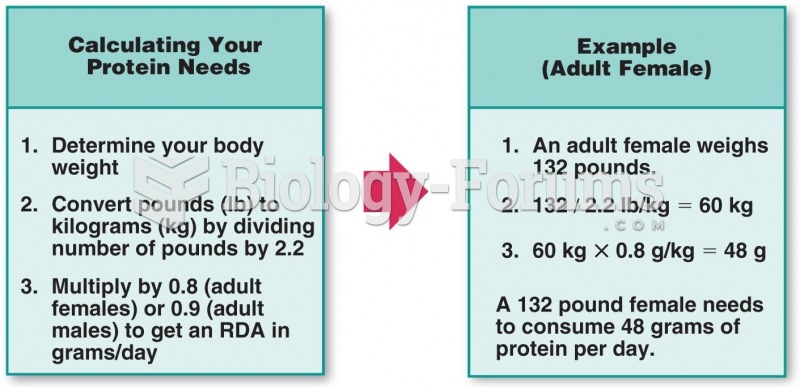
Answer to Question 1
The extent to which foods produce satiation and sustain satiety depends in part on the nutrient composition of a meal. Of the three energy-yielding nutrients, protein is considered the most satiating. In fact, too little protein in the diet can leave a person feeling hungry. Including some proteinsuch as drinking milkprovides satiety and decreases energy intake at the next meal. In contrast, fructose in a sugary fruit drink seems to stimulate appetite and increase food intake.
Foods with a high energy density provide more kcalories, and those with low energy density provide fewer kcalories, for the same amount of food. Foods low in energy density are also more satiating. High-fiber foods effectively provide satiation by filling the stomach and delaying the absorption of nutrients. For this reason, eating a large salad as a first course helps a person eat less during the meal. In contrast, fat has a weak effect on satiation; consequently, eating high-fat foods may lead to passive overconsumption. High-fat foods are flavorful, which stimulates the appetite and entices people to eat more. High-fat foods are also energy dense; consequently, they deliver more kcalories per bite. Although fat provides little satiation during a meal, it produces strong satiety signals once it enters the intestine. Fat in the intestine triggers the release of cholecystokinin a hormone that signals satiety and inhibits food intake.
Eating high-fat foods while trying to limit energy intake requires small portion sizes, which can leave a person feeling unsatisfied. Portion size correlates directly with a food's satiety. Instead of eating small portions of high-fat foods and feeling deprived, a person can feel satisfied by eating large portions of low-fat, high-fiber, and low- energy-density foods.
Answer to Question 2
The basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the rate at which the body expends energy for these life-sustaining activities. The rate may vary from person to person and may vary for the same individual with a change in circumstance or physical condition. The rate is slowest when a person is sleeping undisturbed, but it is usually measured in a room with a comfortable temperature when the person is awake, but lying still, after a restful sleep and an overnight (12 to 14 hour) fast. A similar measure of energy outputcalled the resting metabolic rate (RMR)is slightly higher than the BMR because its criteria for recent food intake and physical activity are not as strict.