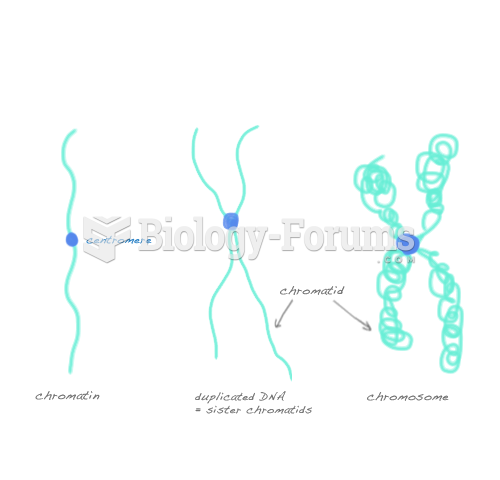
Answer to Question 1
The stomach begins to break down alcohol with its alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme. Women produce less of this stomach enzyme than men; consequently, more alcohol reaches the intestine for absorption into the bloodstream. As a result, women absorb more alcohol than men of the same size who drink the same amount of alcohol. Consequently, they are more likely to become more intoxicated on less alcohol than men. Such differences between men and women help explain why women have a lower alcohol tolerance and a lower guideline for moderate intake.
Answer to Question 2
The liver is the primary site of alcohol metabolism. It can process about ounce of ethanol per hour (the amount defined as a drink), depending on the person's body size, previous drinking experience, food intake, and general health. This maximum rate of alcohol breakdown is determined by the amount of alcohol dehydrogenase available. If more alcohol arrives at the liver than the enzymes can handle, the extra alcohol travels around the body, circulating again and again until liver enzymes are finally available to process it.
The amount of alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme present in the liver varies with individuals, depending on the genes they have inherited and on how recently they have eaten. Fasting for as little as a day prompts the body to degrade its proteins, including the alcohol-processing enzymes, and this can slow the rate of alcohol metabolism by half. Drinking after not eating all day thus causes the drinker to feel the effects more promptly for two reasons: rapid absorption and slowed breakdown.
The alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme breaks down alcohol by removing hydrogens in two steps. In the first step, alcohol dehydrogenase oxidizes alcohol to acetaldehydea highly reactive and toxic compound. High concentrations of acetaldehyde in the brain and other tissues are responsible for many of the damaging effects of alcohol abuse.
In the second step, a related enzyme, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, converts acetaldehyde to acetate, which is then converted to either carbon dioxide (CO2) or acetyl CoAthe compound that plays such a central role in energy metabolism. The reactions from alcohol to acetaldehyde to acetate produce hydrogens (H1) and electrons. The B vitamin niacin, in its role as a coenzyme, helpfully picks up these hydrogens and electrons and escorts them to the electron transport chain.