Answer to Question 1
The electron transport chain captures energy in the high-energy bonds of ATP. The electron transport chain consists of a series of proteins that serve as electron carriers. These carriers are mounted in sequence on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. As the coenzymes deliver their electrons from the TCA cycle, glycolysis, and fatty acid oxidation to the electron transport chain, each carrier receives the electrons and passes them on to the next carrier. These electron carriers continue passing the electrons down until they reach oxygen. Oxygen (O) accepts the electrons and combines with hydrogen atoms (H) to form water (H2O). That oxygen must be available for energy metabolism explains why it is essential to life. As electrons are passed from carrier to carrier, hydrogen ions are pumped across the membrane to the outer compartment of the mitochondria. The rush of hydrogen ions back into the inner compartment powers the synthesis of ATP. In this way, energy is captured in the bonds of ATP. The ATP leaves the mitochondria and enters the cytoplasm, where it can be used for energy.
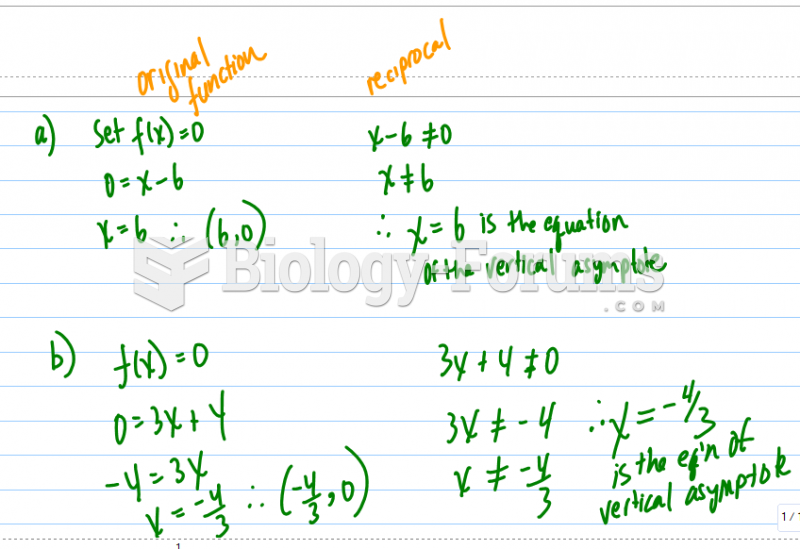
Answer to Question 2
The body cannot store excess amino acids as such; it has to convert them to other compounds. Contrary to popular opinion, a person cannot grow muscle simply by overeating protein. Lean tissue such as muscle develops in response to a stimulus such as hormones or physical activity. When a person overeats protein, the body uses the surplus first by replacing normal daily losses and then by increasing protein oxidation.
Compared with protein, the proportion of carbohydrate in the fuel mix changes more dramatically when a person overeats. The body handles abundant carbohydrate by first storing it as glycogen, but glycogen storage areas are limited and fill quickly. Because maintaining glucose balance is critical, the body uses glucose frugally when the diet provides only small amounts and freely when supplies are abundant. In other words, glucose oxidation rapidly adjusts to the dietary intake of carbohydrate.
Like protein, excess glucose can also be converted to fat directly. This pathway is relatively minor, however. As mentioned earlier, converting glucose to fat is energetically expensive and does not occur until after glycogen stores have been filled. Still, new body fat is made whenever carbohydrate intake is excessive.
Excess dietary carbohydrate can also displace fat in the fuel mix. When this occurs, carbohydrate spares both dietary fat and body fat from oxidationan effect that may be more pronounced in overweight people than in lean people. The net result: excess carbohydrate contributes to obesity or at least to the maintenance of an overweight body.
Unlike excess protein and carbohydrate, which both increase oxidation, eating too much fat does not promote fat oxidation. Instead, excess dietary fat moves efficiently into the body's fat stores; almost all of the excess is stored.