This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.
Did you know?
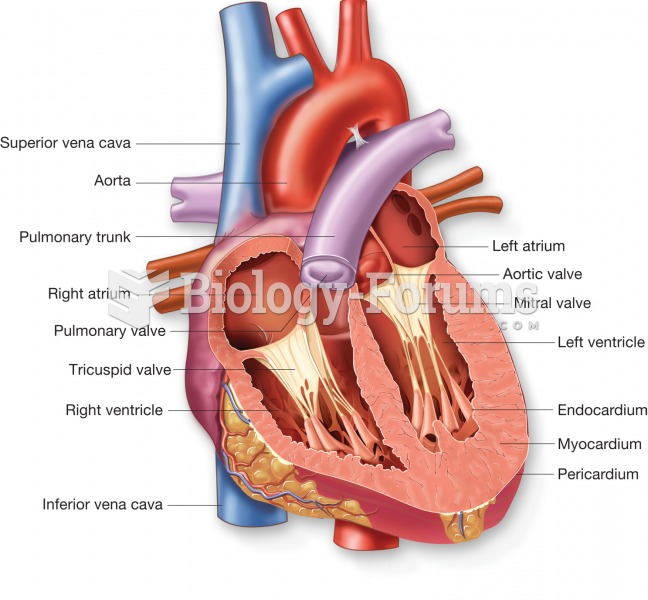
More than nineteen million Americans carry the factor V gene that causes blood clots, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease.
Did you know?
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.
Did you know?
Studies show that systolic blood pressure can be significantly lowered by taking statins. In fact, the higher the patient's baseline blood pressure, the greater the effect of statins on his or her blood pressure.
Did you know?
Bacteria have been found alive in a lake buried one half mile under ice in Antarctica.