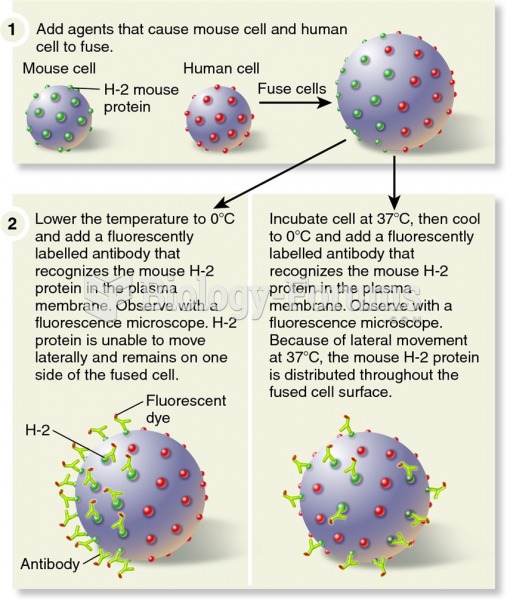
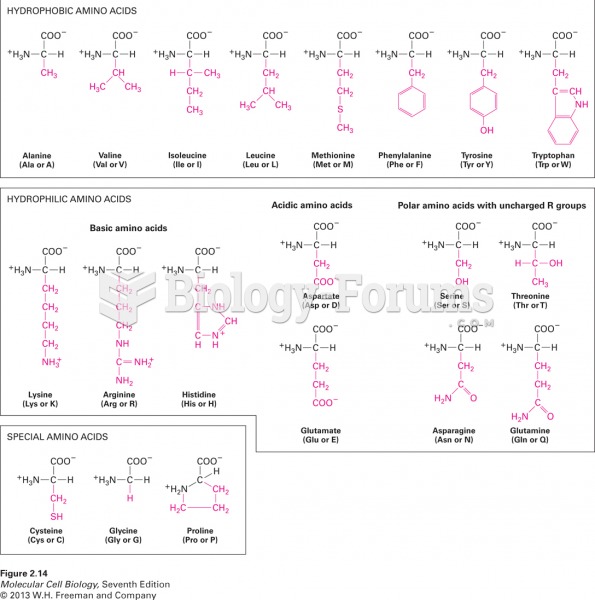
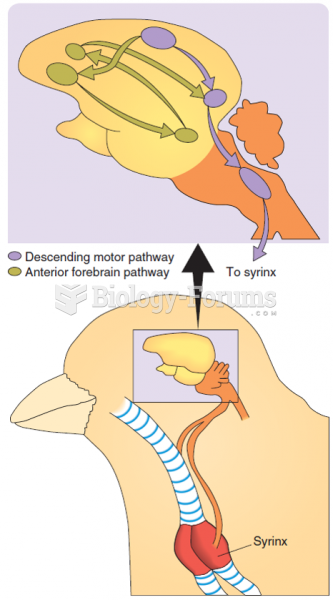
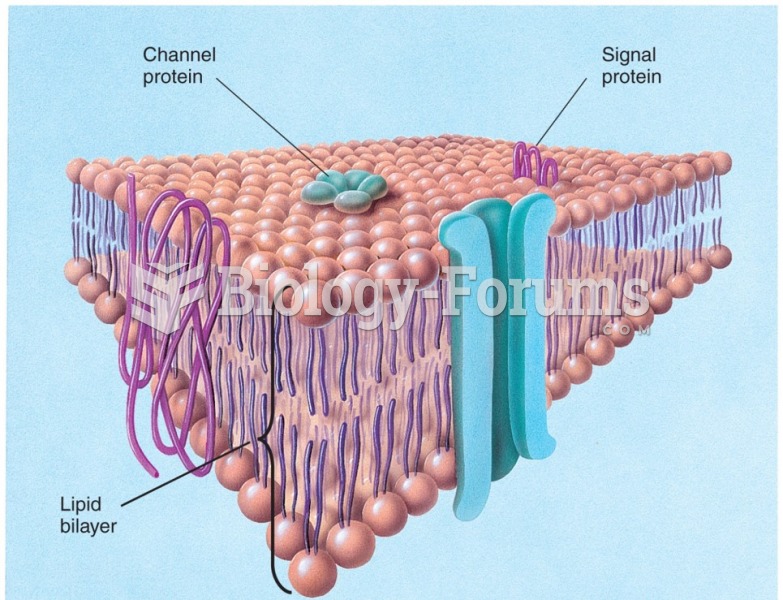
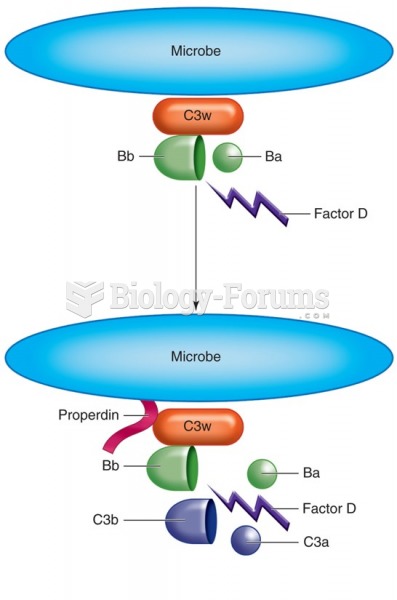
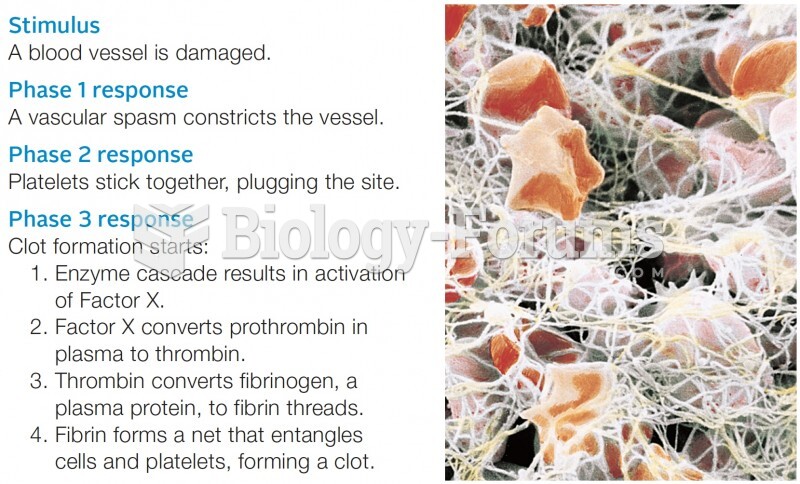
|
|
|
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Once thought to have neurofibromatosis, Joseph Merrick (also known as "the elephant man") is now, in retrospect, thought by clinical experts to have had Proteus syndrome. This endocrine disease causes continued and abnormal growth of the bones, muscles, skin, and so on and can become completely debilitating with severe deformities occurring anywhere on the body.
Historic treatments for rheumatoid arthritis have included gold salts, acupuncture, a diet consisting of apples or rhubarb, nutmeg, nettles, bee venom, bracelets made of copper, prayer, rest, tooth extractions, fasting, honey, vitamins, insulin, snow collected on Christmas, magnets, and electric convulsion therapy.
There are actually 60 minerals, 16 vitamins, 12 essential amino acids, and three essential fatty acids that your body needs every day.