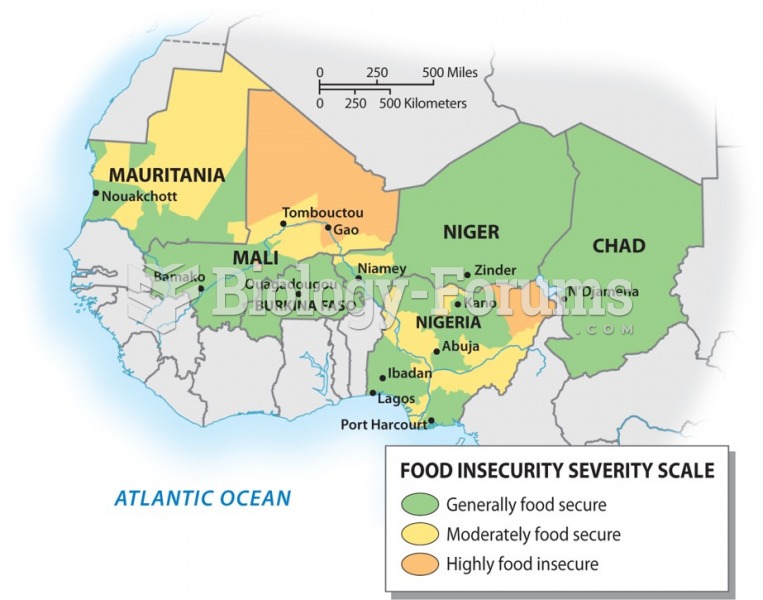
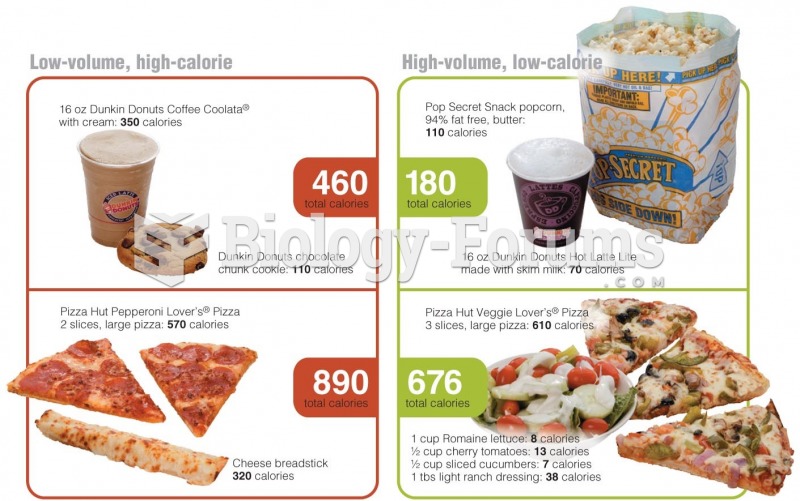
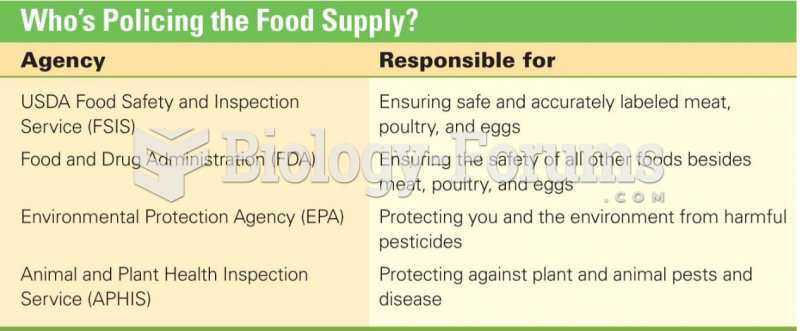
Answer to Question 1
Although the physical responses to a food allergy and food intolerance may be very similar, the difference between the two is whether or not the immune system is involved in the reaction. Food intolerance is far more common than food allergy. A food intolerance is an adverse reaction to food that does not involve the immune system. Lactose intolerance is one example of a food intolerance. A person with lactose intolerance lacks the enzyme needed to digest lactose. When that person eats milk products, symptoms such as gas, cramps, and bloating can occur. Some people may develop sensitivity to various other agents in a food. Tyramine, found in cheese or red wine, can induce a headache in some people. Others may have sensitivity to certain food additives, such as monosodium glutamate (MSG), sulfites, or coloring agents. The physical reactions to these agents can include hives, rashes, nasal congestion, or asthma.
A food allergy, in contrast, is an abnormal response to a food triggered by the immune system. The allergic reaction involves three main components: food allergens, immunoglobulin E (IgE), and mast cells. Food allergens are the fragments of food that are responsible for the allergic reaction. They consist of proteins from the food that are not broken down during the digestive process, which then cross the gastrointestinal lining to enter the bloodstream. IgE is a type of protein called an antibody that circulates through the blood. When allergic people eat certain foods, their immune system reacts to the food allergen by making IgE that is specific to that food. Once released, the IgE antibody attaches to a cell called the mast cell. Mast cells are specialized cells of the immune system that serve as the storehouse for various chemical substances, including histamine. Mast cells are found in all body tissues, but they are especially common in the areas of the body that are typical sites of allergic reaction: the nose and throat, lungs, skin, and gastrointestinal tract. When an allergic reaction occurs, the food allergen interacts with the IgE on the surface of the mast cells, which triggers those cells to release histamine. Depending on the tissue in which the histamine is released, these chemicals will cause a person to have various symptoms of a food allergy. The most severe allergic reaction is anaphylaxis. This potentially fatal condition occurs when several parts of the body experience food allergy reactions at the same time. Signs of anaphylaxis include difficulty breathing, swelling of the mouth and throat, a drop in blood pressure, and loss of consciousness. The reaction can occur in a few seconds or minutes, and without immediate medical attention, death may result. The foods most associated with anaphylactic reactions include peanuts, tree nuts (for example, walnuts, cashews), eggs, and shellfish.
Answer to Question 2
True