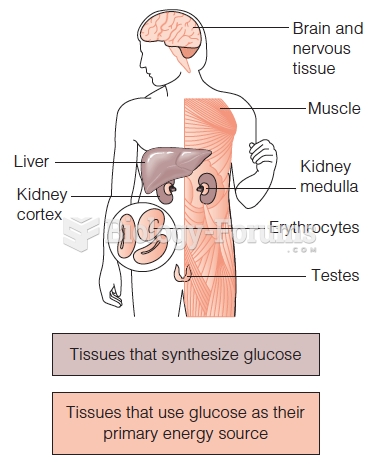
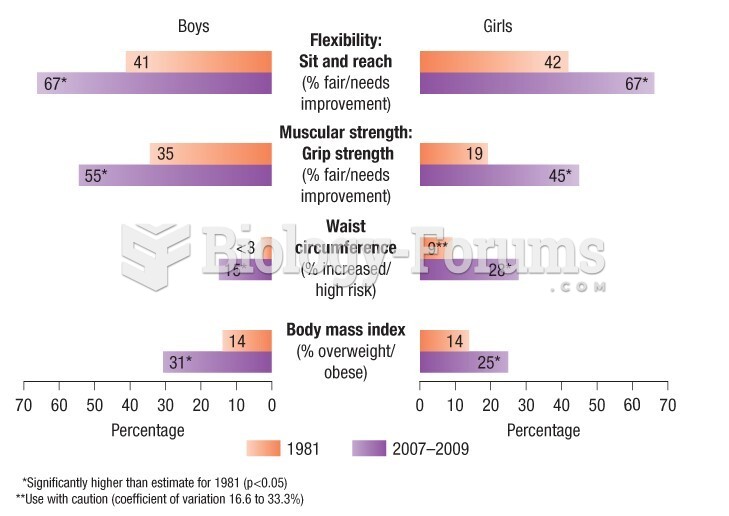
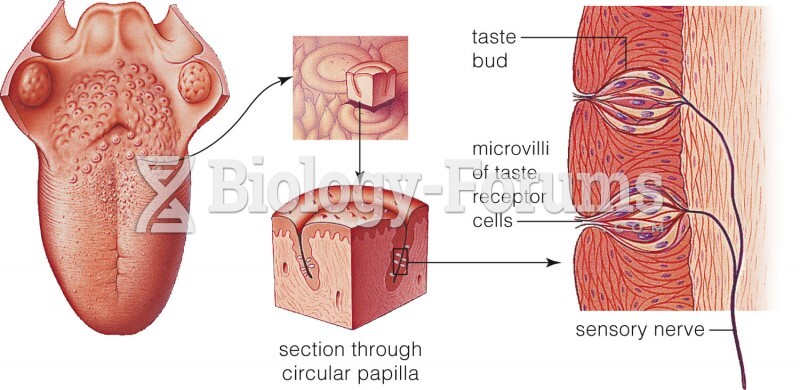
|
|
|
The people with the highest levels of LDL are Mexican American males and non-Hispanic black females.
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.
ACTH levels are normally highest in the early morning (between 6 and 8 A.M.) and lowest in the evening (between 6 and 11 P.M.). Therefore, a doctor who suspects abnormal levels looks for low ACTH in the morning and high ACTH in the evening.
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, more than 50 million Americans have some kind of food allergy. Food allergies affect between 4 and 6% of children, and 4% of adults, according to the CDC. The most common food allergies include shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, fish, eggs, milk, and soy.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.