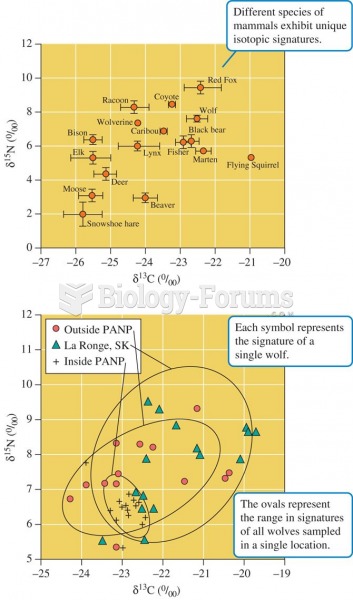
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
Did you know?
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
Did you know?
In 1885, the Lloyd Manufacturing Company of Albany, New York, promoted and sold "Cocaine Toothache Drops" at 15 cents per bottle! In 1914, the Harrison Narcotic Act brought the sale and distribution of this drug under federal control.
Did you know?
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Did you know?
According to animal studies, the typical American diet is damaging to the liver and may result in allergies, low energy, digestive problems, and a lack of ability to detoxify harmful substances.
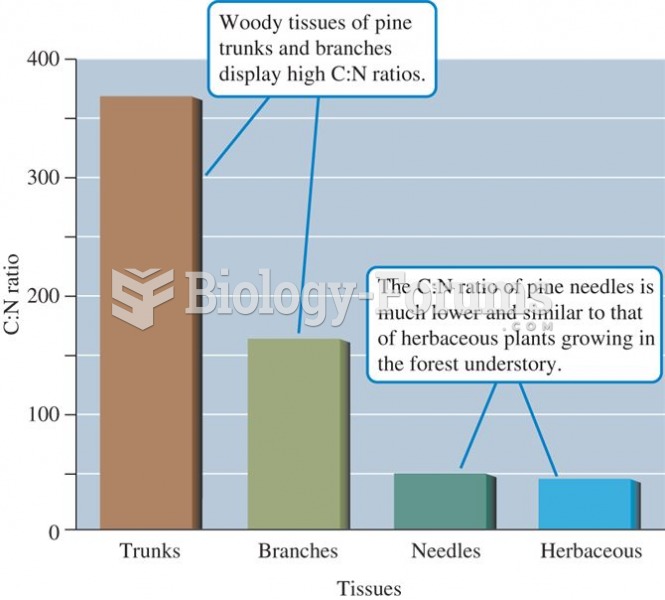 C:N ratios differ a great deal among the tissues of pines and between the woody tissues of pines and
C:N ratios differ a great deal among the tissues of pines and between the woody tissues of pines and
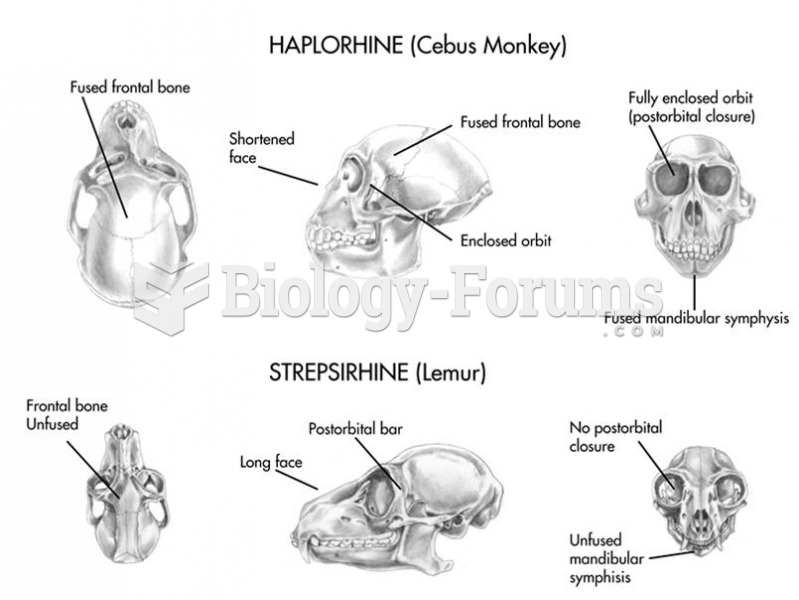 The skulls of living haplorhines differ from those of strepsirhines by having large brains, an enclo
The skulls of living haplorhines differ from those of strepsirhines by having large brains, an enclo