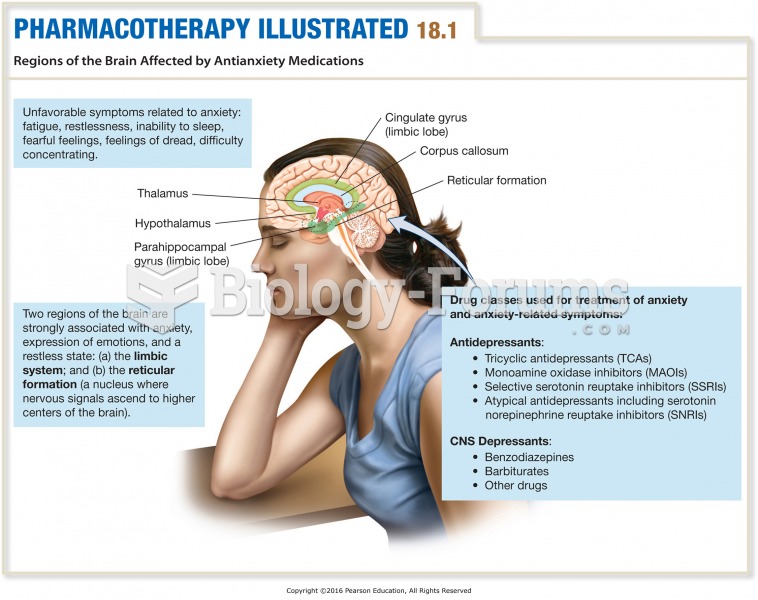
Answer to Question 1
Dyazide is also known as hydrochlorothiazide (thiazide diuretic) combined with triamterene (potassium-sparing diuretic). It works by decreasing the blood volume, which ultimately lowers blood pressure. Dyazide also increases urinary output and inhibits sodium and water reabsorption to help with edema or fluid retention in the extremities.
Side effects:
Hypokalemia,
Hyperlipidemia
Hypertriglyceridemi a
Hypercholesterolemi a
Glucose intolerance
N/V
Anorexia
Dehydration/Dry mouth
Diarrhea
Weakness
Potentially hypotension
Constipation
Drug-nutrient interactions:
Increases potassium excretion, so may need a potassium supplement
Cannot take with NSAIDSs
Avoid licorice
Take with food
Do not take with Ca, Al, Mg, or Fe supplements within 2 hours of medication
Lipitor (trade name for atorvastatin) is a statin drug in the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor class. Therefore, it works on the rate-limiting step of cholesterol production to decrease cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides. It also raises HDL levels 7-30.
Side effects:
Myopathy: muscle pain
Increased liver enzymes
Drug-nutrient interactions:
Cannot be prescribed if patient has liver disease
Cannot take with certain antibiotics, various anti-fungal agents, and P 450 inhibitors (e.g. grapefruit)
Fibrates and niacin should be used with caution
He is also beginning insulin.
Lispro: rapid-acting insulin. Taken with meals to help control high blood glucose levels.
Glargine: basal insulin to help control high blood glucose levels.
Potential side effects: Hypoglycemia
Answer to Question 2
Metformin is a biguanide and is also referred to as Glucophage. It decreases hepatic glucose production or gluconeogenesis and improves insulin resistance by increasing insulin uptake in the muscles. There are very few side effects with metformin, which is why it is commonly used as the initial drug of choice for type 2 diabetes. Hypoglycemia is not a side effect with metformin like it is with the other glucose-lowering medications.
Potential side effects:
Diarrhea
Nausea
Bloating
Anorexia
Flatulence
Lactic acidosis (although this is very rare)
Drug-nutrient interactions:
Decreases folate and vitamin B12 absorption (may need supplementation of these vitamins)
Avoid alcohol
Needs to be taken with meals to help avoid GI distress or symptoms of nausea, diarrhea, flatulence, etc.
Glyburide is a second-generation sulfonylurea agent. Sulfonylurea drugs work by stimulating insulin secretion from the beta cells of the pancreas. It can only be used in individuals with type 2 diabetes because insulin production is necessary in order for the mechanism of this drug to be effective. Hypoglycemia can be a potential side effect when using sulfonylurea drugs, especially glyburide. Hypoglycemia is the main side effect associated with this medication (weight gain and contraindicated with renal insufficient patients, too). Since glyburide increases insulin secretion, more than enough insulin may be released into the blood, which can lead to hypoglycemia.
Drug-nutrient interactions: Avoid alcohol; take once before breakfast (30-60 min. prior)
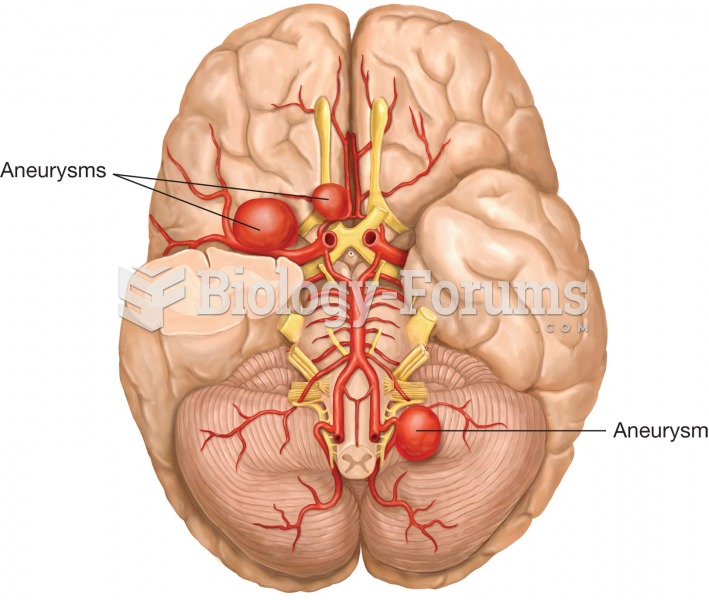 Cerebral aneurysm. A cerebral aneurysm is the abnormal dilation of arteries supplying the brain, whi
Cerebral aneurysm. A cerebral aneurysm is the abnormal dilation of arteries supplying the brain, whi
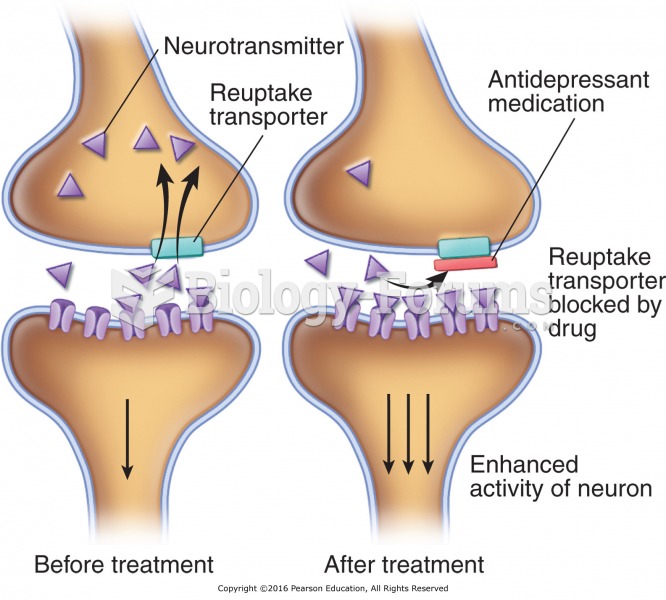 Mechanisms of action of antidepressants: (a) In adrenergic and serotonergic neurons the activity of ...
Mechanisms of action of antidepressants: (a) In adrenergic and serotonergic neurons the activity of ...