This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
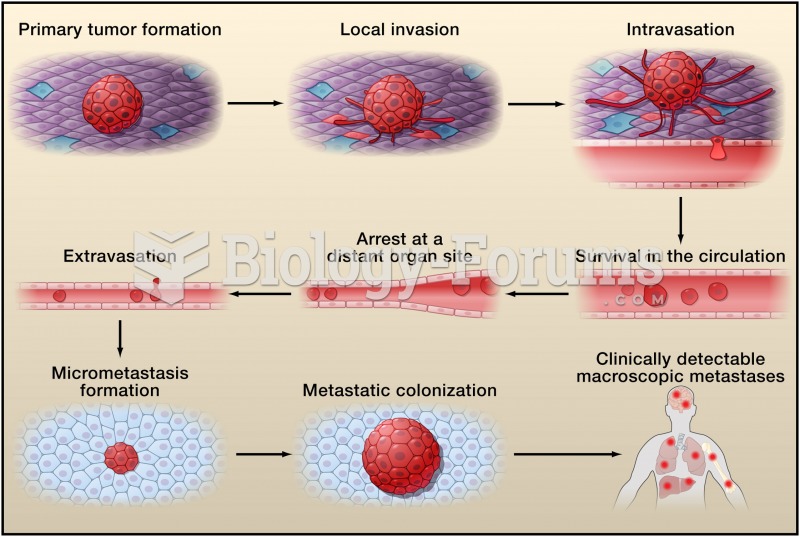
It is widely believed that giving a daily oral dose of aspirin to heart attack patients improves their chances of survival because the aspirin blocks the formation of new blood clots.
Did you know?
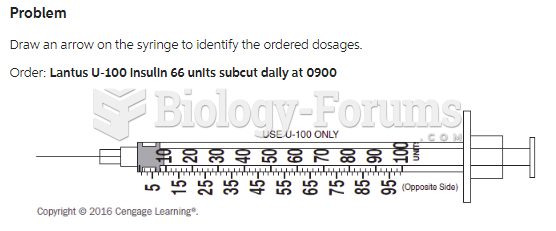
Medication errors are more common among seriously ill patients than with those with minor conditions.
Did you know?
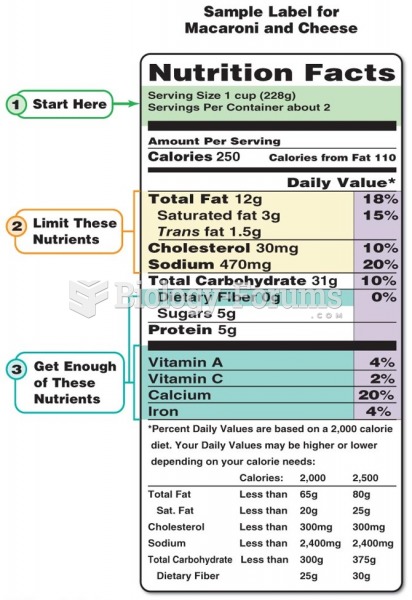
According to the CDC, approximately 31.7% of the U.S. population has high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" levels.
Did you know?
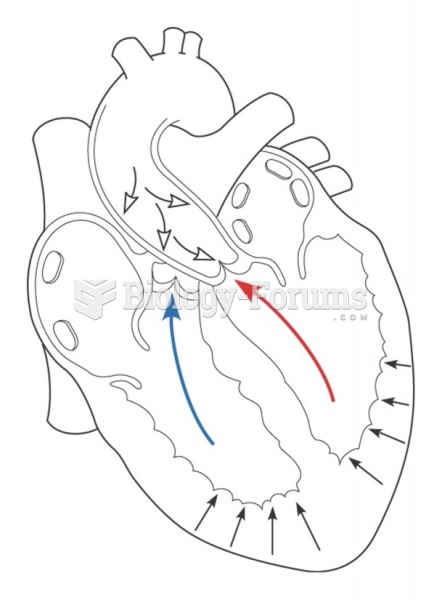
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
Did you know?
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.