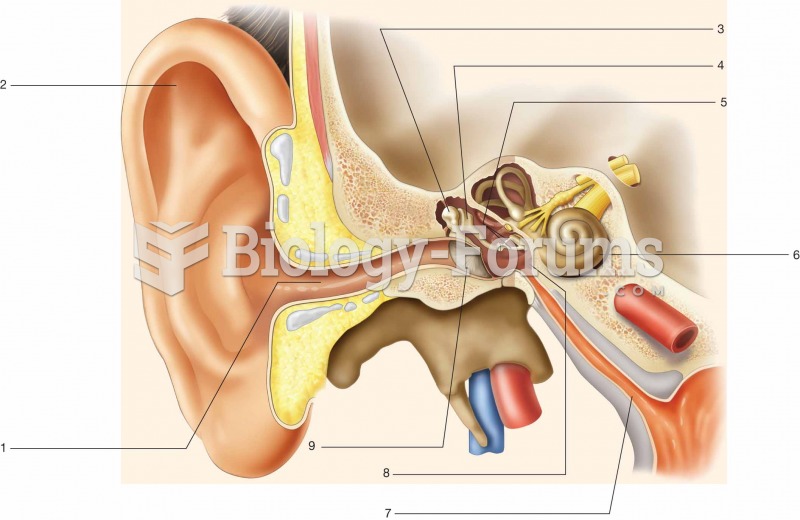
Answer to Question 1
Potassium: high d/t fluid shifts and sodium/potassium balance
Glucose: high d/t gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis from inflammatory response (pt also has history of T2 diabetes)
Phosphate: fluid shifts and electrolyte balance
Protein, albumin, prealbumin: low because these are negative acute-phase proteins and synthesis rate decreases during metabolic stress
CPK: a cell isoenzyme that can be elevated with systemic inflammation
ALT, AST, Lactate dehydrogenase: elevated due to potential damage from sepsis (e.g. leukocytes damaging the hepatocellular membranes, apoptosis related to the immune response, or tissue ischemia due to microvascular obstruction).
Cholesterol, LDL, TGs: increased d/t increased lipolysis during inflammatory response (pt also has PMH of hyperlipidemia)
WBC: indicator of infection; leukocytes destroy and remove foreign materials, microorganisms, and cell debris
HbA1C: elevated due to T2DM
Hgb, Hct: low d/t recent resection of stomach and decreased area for absorption of iron
CRP: acute-phase protein increased with inflammation
Fibrinogen: acute-phase protein increased with inflammation
Lactate: byproduct of lipolysis that accumulates in the blood during the inflammatory response and is an indicator for tissue hypoxia; is a marker for metabolic stress
Ferritin (low)/Transferrin (high): due to iron-deficiency anemia from malabsorption from Roux-en-Y
Answer to Question 2
Flu-like symptoms, nausea: associated with the infection and inflammatory response
Acutely short of breath: fluid overload due to inflammatory response and third-spacing of fluids
The shift of fluid into the lungs and other third spaces occurs due to the increased vascular permeability consistent with the inflammatory response.
Mechanical ventilation: difficulty breathing due to accumulation of fluid and inflammatory response
Temp 102.5, heart rate 98, respiratory rate 23: consistent with inflammation and sepsis
2+ pitting edema: indication of third spacing and fluid overload
Ecchymosis, petechiae: indicators of internal hemorrhaging, potentially caused by fluid overload and vascular permeability
Rapid respirations with rales: the excess fluid in the lungs can cause the rales
Diminished pulses bilaterally: with increased fluid retention, pulses become more difficult to palpate