Answer to Question 1
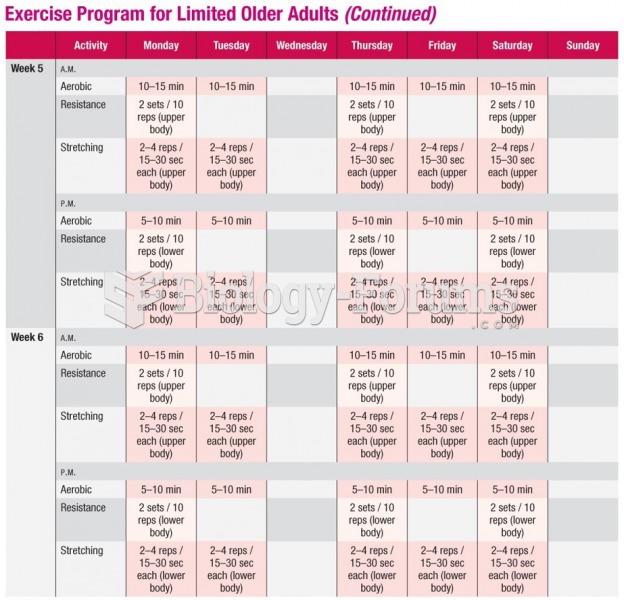
Mr. McKinley should adhere to an exercise routine that he enjoys.
To assess readiness, see what he is willing to do and establish goals. Goals should be attainable, realistic, and concrete.
Consider social support via group activities/teams/sports leagues and a personal trainer, as needed.
Strenuous exercise should be avoided until he is healed, but walking should not be avoided.
Physician should be consulted to discuss exercise options that are appropriate.
Exercise will help maintain weight loss over time because after the weight is lost, Mr. McKinley will have to change his lifestyle to maintain weight loss.
Exercise will help with chronic conditions such as obesity, hypertension (reduces BP), and diabetes. There is evidence that exercise improves insulin resistance.
Once an exercise program is in place, Mr. McKinley will still have to follow up with a physician or exercise specialist to assess any medical problems associated with exercise such as chest pain, dyspnea, etc.
Answer to Question 2
Limited adherence to nutrition-related recommendations related to (additional information needs to be gathered from a nutrition assessment and interview) as evidenced by patient stating that she tried to follow the diet that she was taught 2 years ago but it was hard to keep up
- Ideal Goal: Patient able to sustain changes in diet based on recommendations for dialysis
- Intervention: Nutrition counseling that includes purpose of dietary changes consistent with nutritional consequences of chronic kidney disease and treatment with dialysis; assess readiness and self-efficacy for change. Strategies to include motivational interviewing, self-monitoring, and problem solving.
Inadequate protein-energy intake related to recent poor appetite and nausea and vomiting secondary to CKD as evidenced by typical recent daily intake of 1300 kcal and 64 g protein compared to recommended 2450 kcal and 72 g protein (hemodialysis)
- Ideal Goal: Patient will meet protein/energy requirements.
- Intervention: Nutrition education of appropriate foods rich in high-biological value protein (e.g. meat, egg, etc.) and calories without conflicting with Na, K, and P restrictions.
Inappropriate intake of carbohydrates (sugars) related to drinking of sweetened cola as evidenced by typical daily intake of sugars providing 17 of total kcal
Inappropriate intake of fats (cholesterol) related to intake of meats and eggs as evidenced by typical dietary intake of cholesterol greater than 300 mg
Undesirable food choices related to (additional information needs to be gathered from a nutrition assessment and interview) as evidenced by consumption of higher-sodium foods such as processed meats, potato chips, and crackers
- Ideal Goals: Nutrition prescription: Diet Rx: 35 kcal/kg, 1.2 g protein/kg, 2 g K, 1 g phosphorus, 2 g Na, 1,000 mL fluid + urine output per day; decrease sodium and cholesterol intake
- Intervention: Comprehensive nutrition education for modifications. Based on patient preferences, will use renal exchange lists to assist in meal planning and food selection. Provide detailed list of foods that are high in sodium with alternatives to improve taste.
Overweight related to fluid imbalance and edema as evidenced by 4 kg weight gain 2 weeks prior to admit and BMI of 33.3 (adjusted edema-free weight of BMI 31.5)
Altered nutrition-related laboratory values related to inappropriate intake of sugars as evidenced by BG of 282 and A1c 8.9 (the etiology may need to be further examined; it could be related to medication dosage, infection, etc.)
- Ideal Goal: Stabilization of weight and normalization of BG and A1c.
- Intervention: Will provide instruction for recording food intake and BG. Instruction on purpose of tracking daily intake of fluid and weight. Stress the importance of her adherence to her oral diabetic medications.