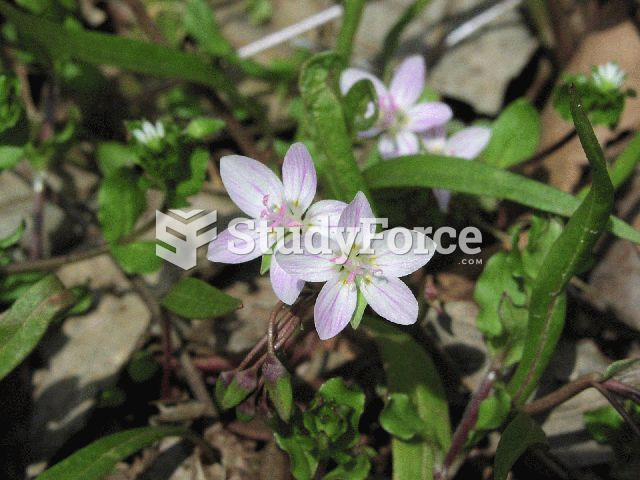
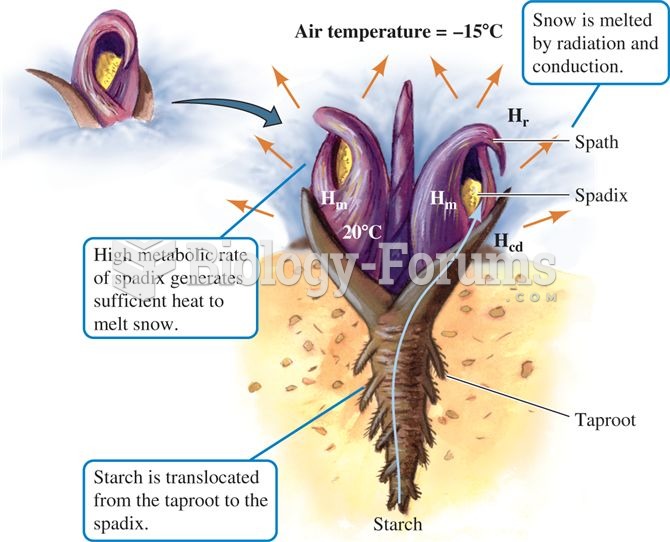
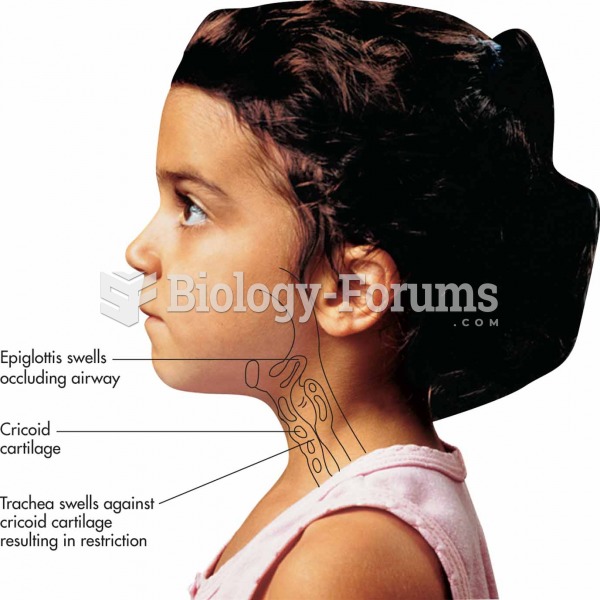
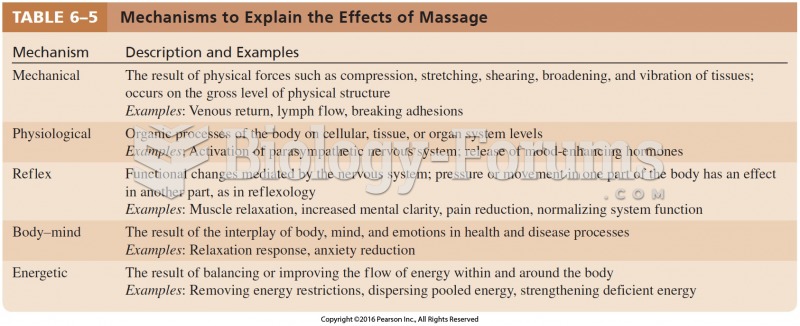
Answer to Question 1The ocean responds simultaneously to inertia and to the gravitational force of both the sun
and moon. If Earth, moon, and sun are all in a line, the lunar and solar tides will be additive,
resulting in higher high tides and lower low tides. The large tides caused by the linear
alignment of the sun, Earth, and moon are called spring tides. During spring tides, high tides
are very high and low tides very low. These tides occur at 2-week intervals corresponding to the new and full moons. But if the moon, Earth, and sun form a right angle, the solar tide
will tend to diminish the lunar tide. Because the moons contribution is more than twice that
of the sun, the solar tide will not completely cancel the lunar tide. Neap tides occur when the
moon, Earth, and sun form a right angle. During neap tides, high tides are not very high and
low tides not very low. Neap tides also occur at 2-week intervals, with the neap tide arriving
a week after the spring tide
Answer to Question 2cWater moving in a tide wave tends to stay to the right of an ocean basin due to the Coriolis
effect. As water moves north in a Northern Hemisphere ocean, it moves toward the eastern
boundary of the basin; as it moves south, it moves toward the western boundary. A wave
crest moving counterclockwise will develop around a node if this motion continues to be
stimulated by tidal forces. The node (or nodes) near the center of an ocean basin is called an
amphidromic point. An amphidromic point is a no-tide point in the ocean, around which the
tidal crest rotates through one tidal cycle. Amphidromic circulation develops as follows (in
the Northern Hemisphere): (1) A tide wave crest enters an ocean basin. (2) The wave trends
to the right, causing a high tide on the basin's eastern shore. (3) Unable to continue turning to
the right because of the interference of the shore, the crest moves northward, following the
shoreline and causing a high tide on the basin's northern shore. (4) The wave continues its
progress around the basin in a counterclockwise direction, forming a high tide on the western
shore and competing the circuit. The point around which the crest moves is an amphidromic
point.