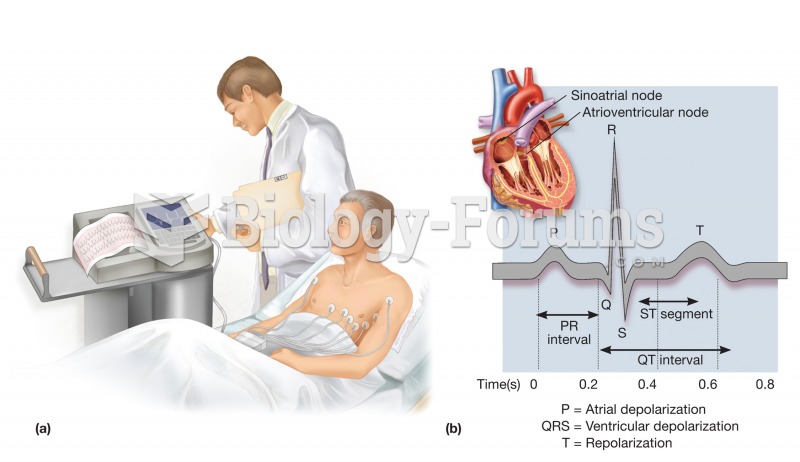
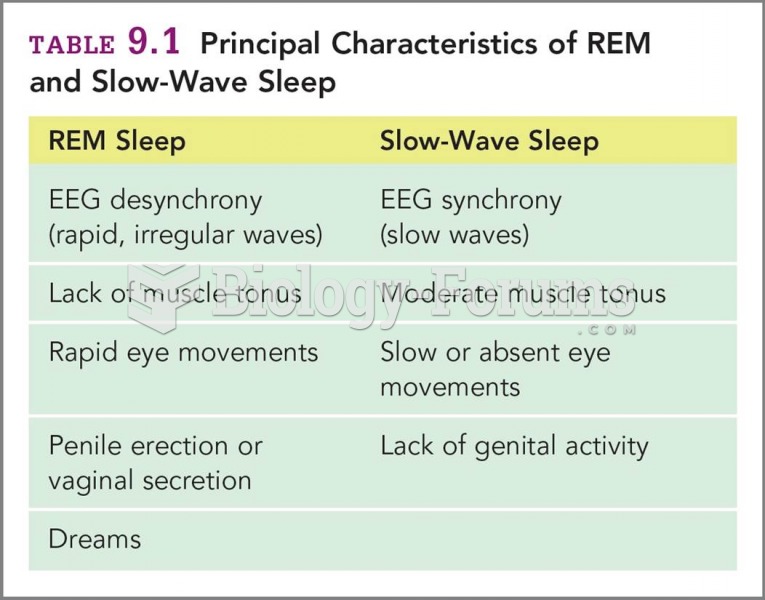
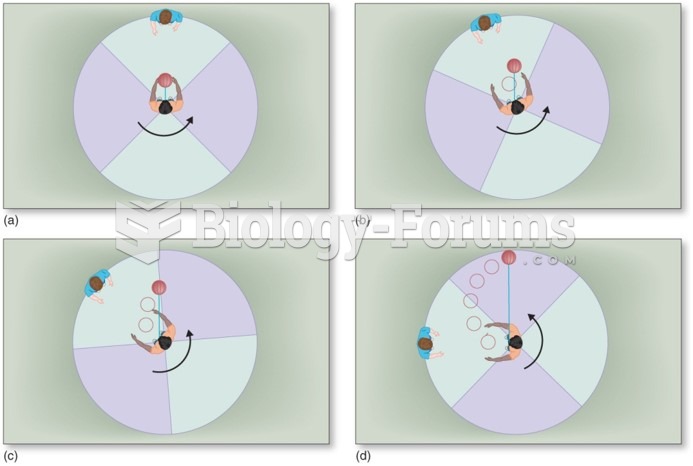
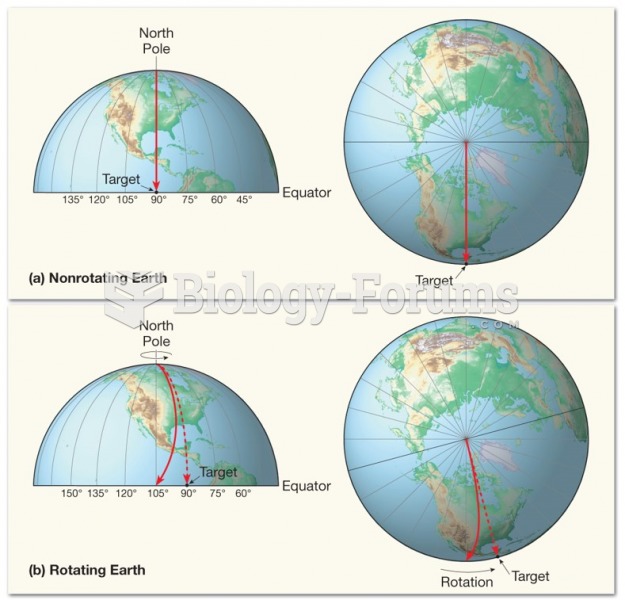
|
|
|
People about to have surgery must tell their health care providers about all supplements they take.
Although puberty usually occurs in the early teenage years, the world's youngest parents were two Chinese children who had their first baby when they were 8 and 9 years of age.
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
There are over 65,000 known species of protozoa. About 10,000 species are parasitic.