Answer to Question 1ANS:Answer
should include:
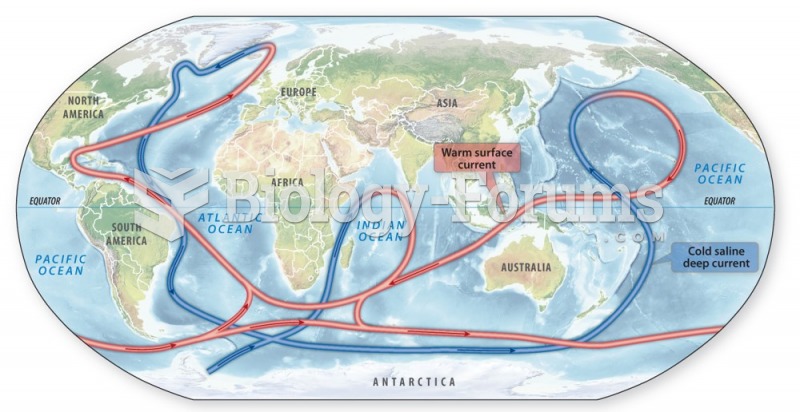
The ocean acts as a reservoir for carbon dioxide because it is able to store large amounts
of it. There is a high theoretical maximum for carbon dioxide which is not reached in the
ocean. There is 60 times the amount of carbon dioxide in the ocean than there is in the
atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide is highly soluble in water. It can move from the atmosphere to the ocean
quite quickly, but is slower in moving from the ocean to the atmosphere.
Marine photosynthesis can quickly use carbon dioxide that enters the water.
Carbon dioxide can re-enter ocean and atmosphere cycles via a few processes.
Sediments can dissolve back into the water. This can happen because of the pH levels in
an area. Geological uplift can expose carbonate rocks to oxygen reactions above water.
These reactions can release the carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Acid rain
achieves the same result when hitting limestone sediments.
Answer to Question 2ANS:Answer
should include:
The ocean contains all the elements that are found in the Earth's crust. These elements
are in different concentrations in the ocean.
Major constituents are the most abundant elements in the ocean. These are the majority
of dissolved inorganic solids which make up the salinity of the ocean. The most
abundant ions in the ocean include chlorine, sodium, sulfate, magnesium, calcium,
potassium and bicarbonate.
Minor constituents are those that have a higher concentration than 1 part per million, but
are not considered abundant. Examples of minor constituents are: bromine, strontium,
boron, silicon, and fluorine.
Trace elements are those that are in less than 1 part per million concentrations in the
ocean. There are 14 important trace elements that are essential for the processes of life.
These trace elements include nitrogen, lithium, iodine, phosphorus, zinc, iron,
aluminum, manganese, lead, mercury and gold.