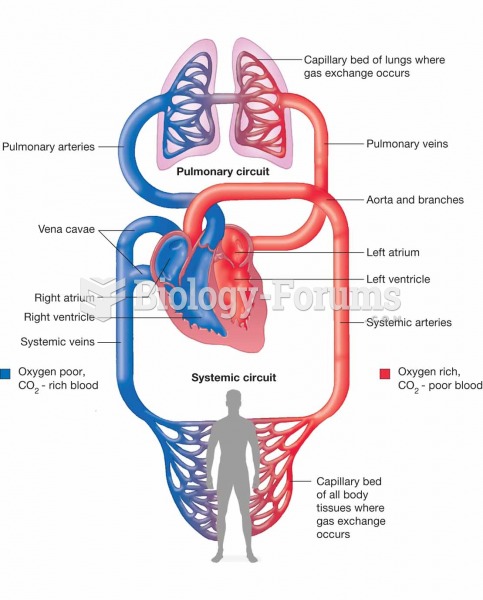
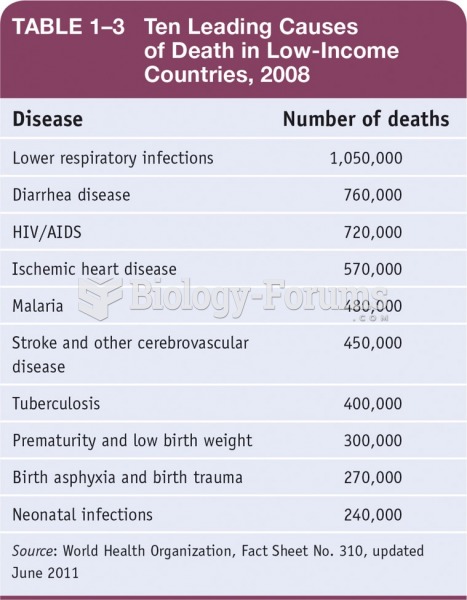
|
|
|
During pregnancy, a woman is more likely to experience bleeding gums and nosebleeds caused by hormonal changes that increase blood flow to the mouth and nose.
The calories found in one piece of cherry cheesecake could light a 60-watt light bulb for 1.5 hours.
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).