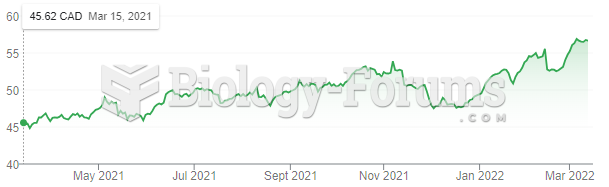
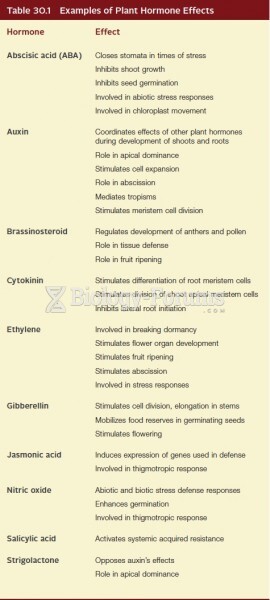
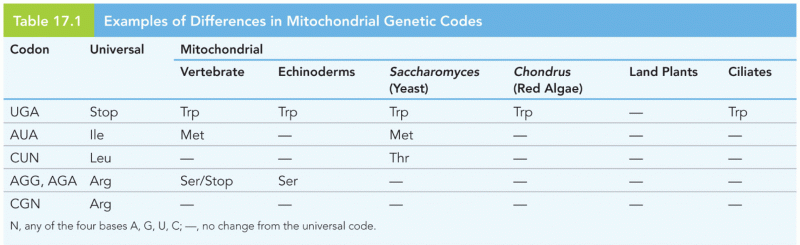
|
|
|
There can actually be a 25-hour time difference between certain locations in the world. The International Date Line passes between the islands of Samoa and American Samoa. It is not a straight line, but "zig-zags" around various island chains. Therefore, Samoa and nearby islands have one date, while American Samoa and nearby islands are one day behind. Daylight saving time is used in some islands, but not in others—further shifting the hours out of sync with natural time.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Approximately 15–25% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, many miscarriages often occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.
The largest baby ever born weighed more than 23 pounds but died just 11 hours after his birth in 1879. The largest surviving baby was born in October 2009 in Sumatra, Indonesia, and weighed an astounding 19.2 pounds at birth.