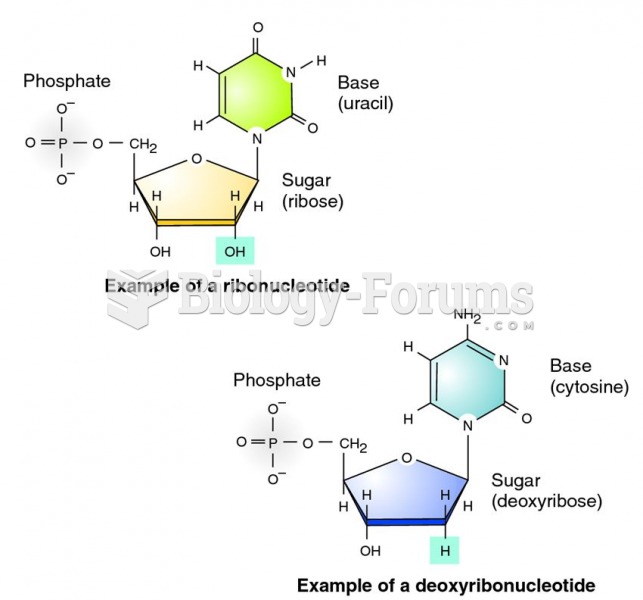
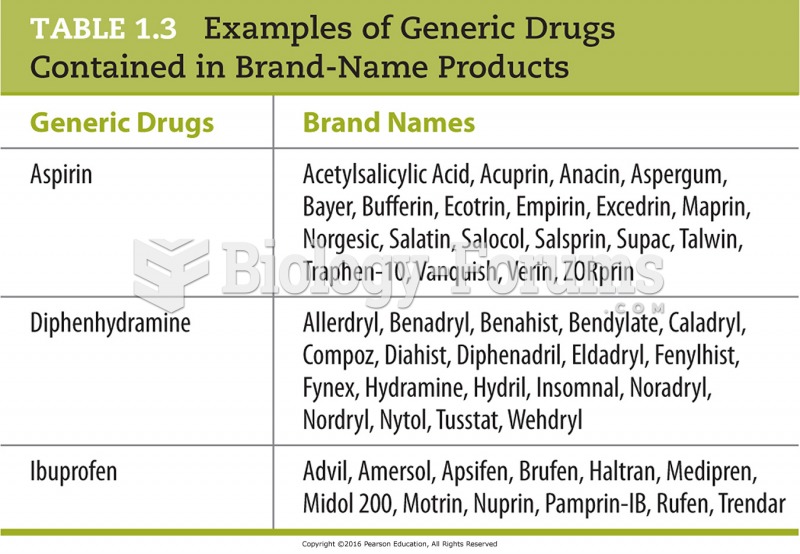
Answer to Question 1
There are two approaches to pain management: pharmalogical and nonpharmalogical.
Often times these approaches are used together to provide maximum pain relief. Pharmalogical approaches include narcotic and nonnarcotic medications.
Nonnarcotics are used for mild to moderate pain, whereas narcotics are used for severe pain. Nonnarcotics include drugs such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen. However, these must be monitored in the patient closely because they may cause toxic side effects in older adults. Narcotic drugs that work well in older adults include morphine and codeine. These must be monitored for side effects as well. There are also many nonpharmalogical approaches to pain management. These
include acupuncture, acupressure, therapeutic touch, the use of heat and/or cold, various ointments, relaxation techniques, and meditation. All the techniques mentioned have advantages and disadvantages. What works for one person might be different than what works for another.
Answer to Question 2
Verbrugge and Jett (1994) proposed a comprehensive model of disability resulting from chronic health conditions. The main path emphasizes the relationships between the person's chronic condition, impairments of organ systems, functional limitations in the person's ability to perform tasks, and disability. The model also considers the impact of any risk factors. Risk factors are behaviors or conditions that may increase one's chances of functional limitation or disability. Risk factors are variables such as low socioeconomic status and health-related behaviors such as smoking. Finally, the model considers the impact of two types of intervention strategies: extraindividual factors and intraindividual factors. Examples of extraindividual factors include handicap accessible ramps, surgery, and social support services such as Meals on Wheels. Intraindividual interventions include such factors as starting an exercise program and keeping a positive attitude. Both intra- and extraindividual factors may help people live more independent lives.