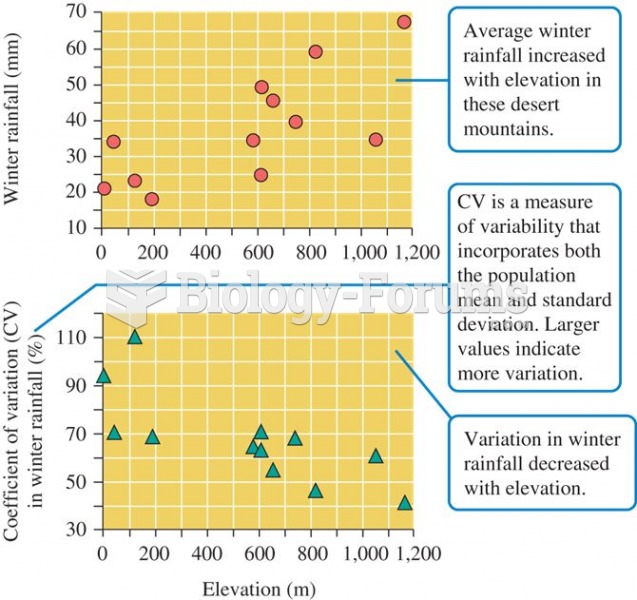
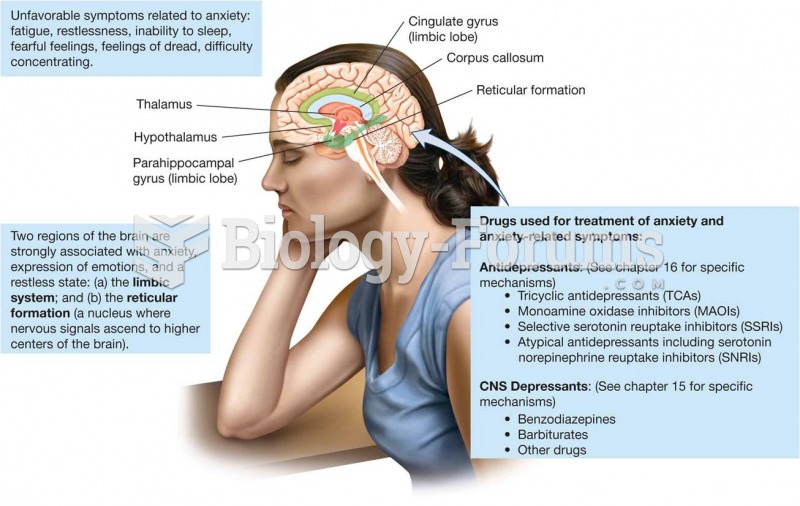
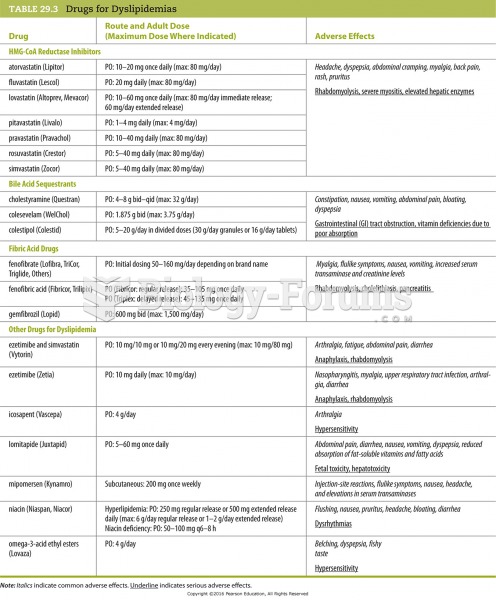
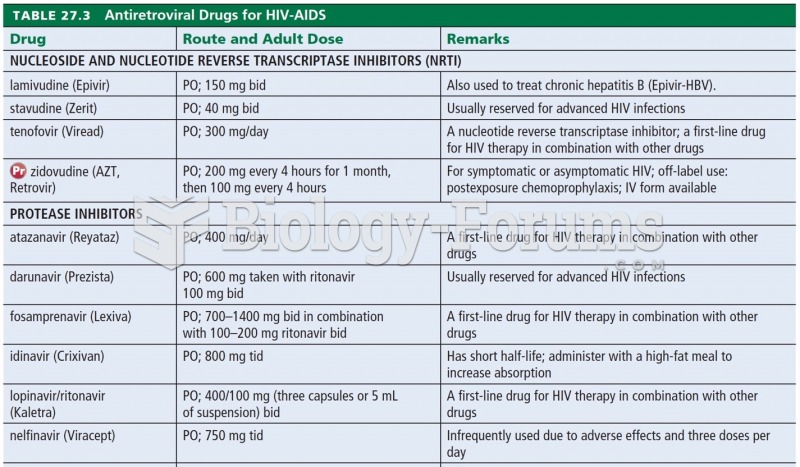
|
|
|
Most women experience menopause in their 50s. However, in 1994, an Italian woman gave birth to a baby boy when she was 61 years old.
If all the neurons in the human body were lined up, they would stretch more than 600 miles.
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
The top five reasons that children stay home from school are as follows: colds, stomach flu (gastroenteritis), ear infection (otitis media), pink eye (conjunctivitis), and sore throat.