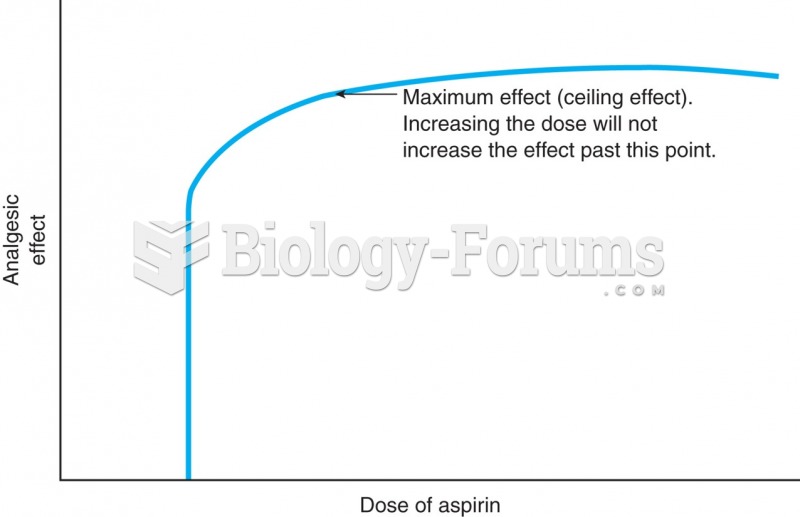
For the following reaction, increasing the pressure will cause the equilibrium to ________.
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2 SO3 (g) + heat
A) shift to the right, towards products
B) shift to the left, towards reactants
C) remain unchanged, but the reaction mixture will get warmer
D) remain unchanged, but the reaction mixture will get cooler
E) Pressure has no effect on equilibrium.
Question 2
If we add a catalyst to the following equation, CO + H2O + heat CO2 + H2, which way will the equilibrium shift?
A) to the left
B) no effect
C) to the right
D) not enough information
Question 3
Diatomic nitrogen is added to the equilibrium system:
N2 (g) + H2 (g) 2 NH3(g) + heat
When a new equilibrium is established the concentration of H2 will be ________ the amount at the original equilibrium, and the amount of NH3 will be ________ the amount at the original equilibrium.
A) greater than; greater than
B) greater than; less than
C) less than; greater than
D) less than; less than
E) Both changes will be impossible to determine.
Question 4
Which change to this reaction system would cause the equilibrium to shift to the right?
N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g) + heat
A) addition of a catalyst
B) addition of NH3 (g)
C) removal of H2 (g)
D) heating the system
E) lowering the temperature
Question 5
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2 SO3 (g) + heat K = 4.8 1027
Which statement about this system is not true?
A) At equilibrium SO3 is the predominant substance.
B) Heating the system will cause breakdown of SO3.
C) Adding SO2 will cause an increase in the amount of SO3.
D) Removing O2 will cause an increase in the amount of SO3.
E) The large value of K means that the reaction essentially goes to completion.
Question 6
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction below if a tank was found to contain 0.106 M O2, 0.00652 M SO3 and 0.00129 M SO2.
2 SO3 (g) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
A) 6.78 10-2
B) 1.34 10-2
C) 4.15 10-3
D) 4.35 10-2
Question 7
When a reaction system is at equilibrium
A) there is no more chemistry happening.
B) the amounts of reactants and products are exactly equal.
C) the reaction rate in the forward direction is at a maximum.
D) the reaction rate in the reverse direction is at a minimum.
E) the rates of the reaction in the forward and reverse directions are exactly equal.