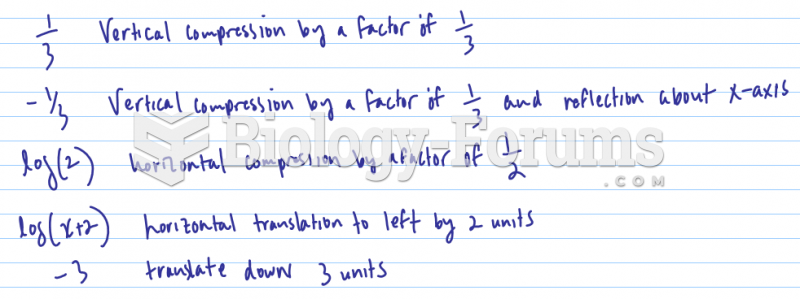
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.
Did you know?
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
Did you know?
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.
Did you know?
Human neurons are so small that they require a microscope in order to be seen. However, some neurons can be up to 3 feet long, such as those that extend from the spinal cord to the toes.
Did you know?
The National Institutes of Health have supported research into acupuncture. This has shown that acupuncture significantly reduced pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, when used as a complement to conventional therapies.



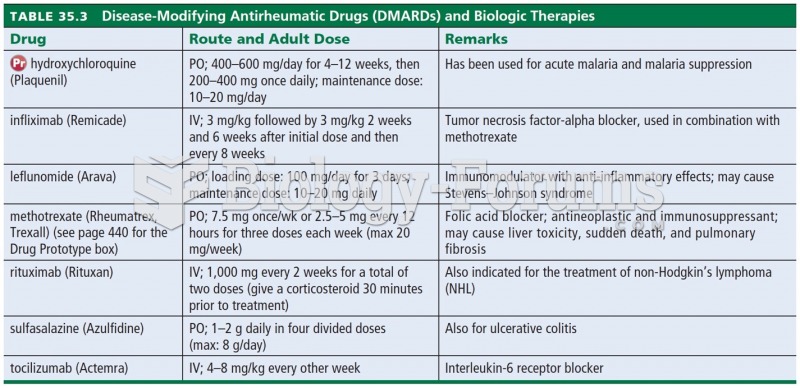
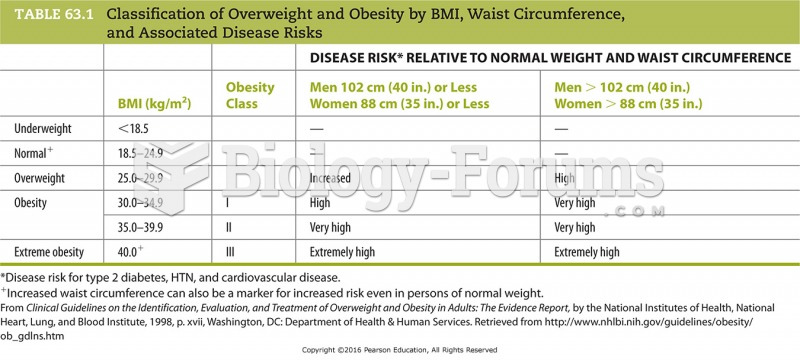
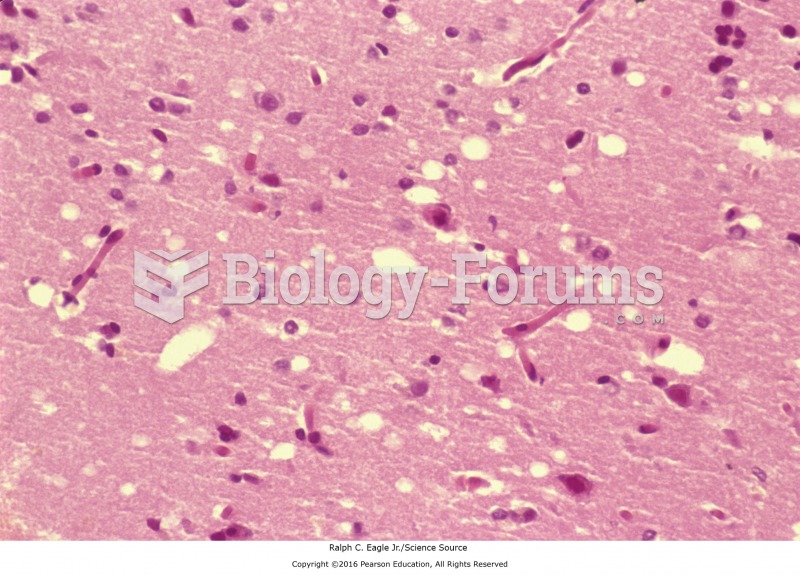
![Chickenpox rash. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC]/Ann Cain)](https://biology-forums.com/gallery/30/medium_548020_08_06_17_10_52_37_306981954.jpeg)