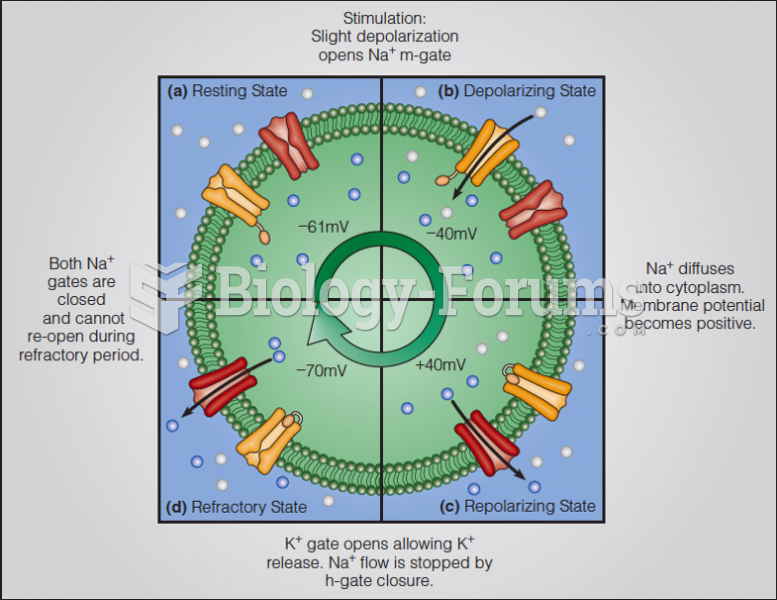
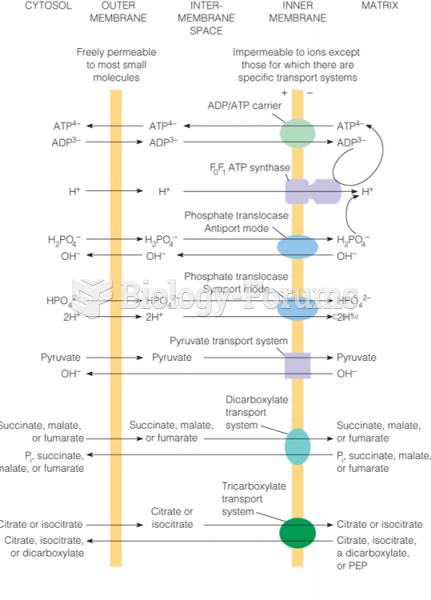
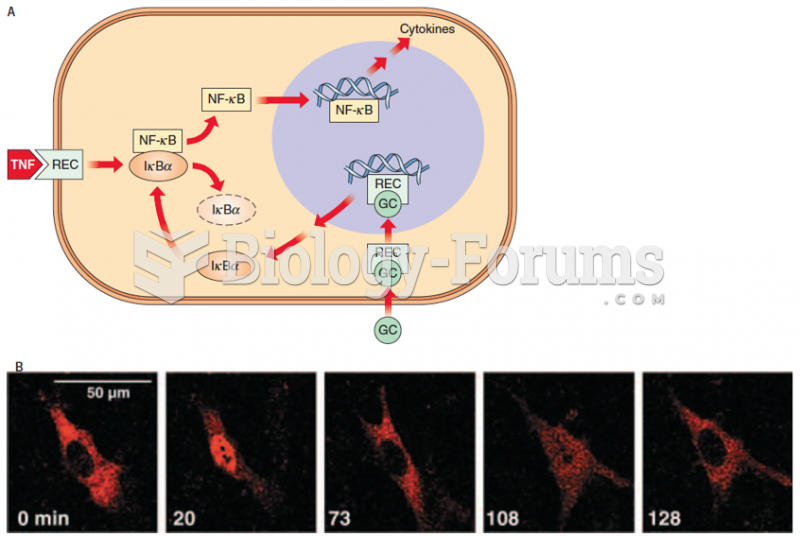
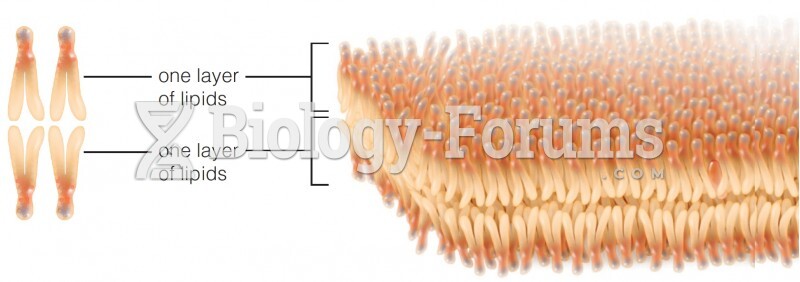
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.
Did you know?
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
Did you know?
The types of cancer that alpha interferons are used to treat include hairy cell leukemia, melanoma, follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma.
Did you know?
The Babylonians wrote numbers in a system that used 60 as the base value rather than the number 10. They did not have a symbol for "zero."
Did you know?
Complications of influenza include: bacterial pneumonia, ear and sinus infections, dehydration, and worsening of chronic conditions such as asthma, congestive heart failure, or diabetes.
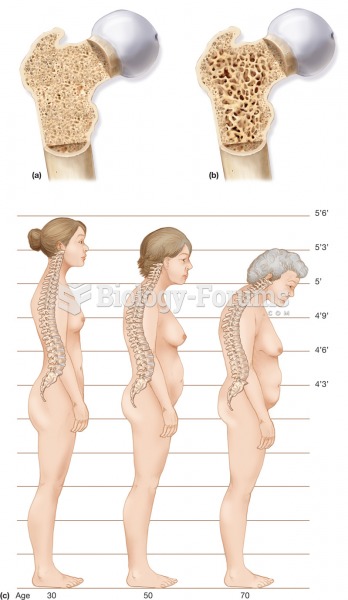 Osteoporosis. (a) A section through normal spongy bone. (b) A section through a bone with osteoporos
Osteoporosis. (a) A section through normal spongy bone. (b) A section through a bone with osteoporos
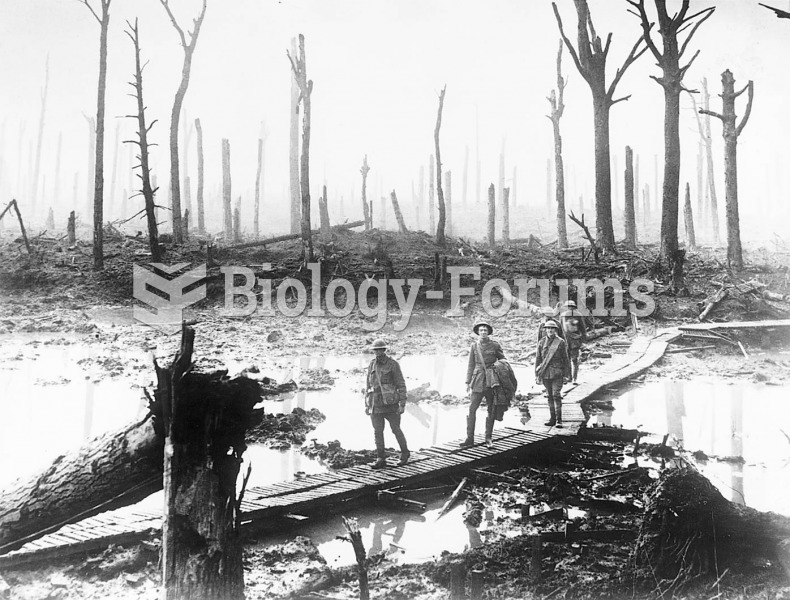 During World War I, advancing armies unloosed ferocious artillery barrages to destroy deeply entrenc
During World War I, advancing armies unloosed ferocious artillery barrages to destroy deeply entrenc