Answer to Question 1
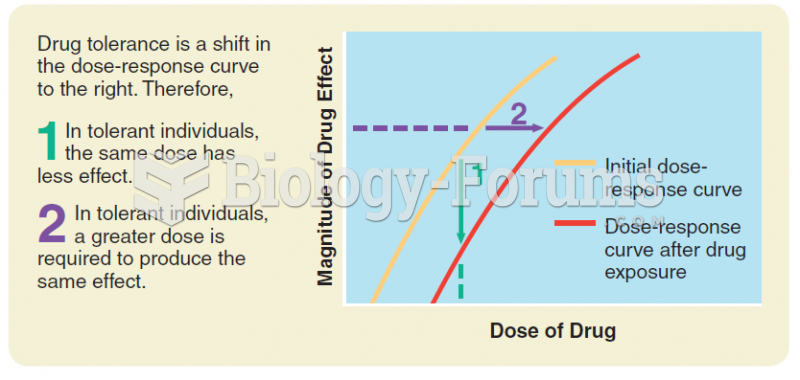
Context-specific tolerance refers to a decrease in response to a drug primarily resulting from learning processes, in which the contextual stimuli become CSs for compensatory CRs that reduce the apparent drug-induced reactions (UCRs), or the organism learns instrumental compensatory responses to behaviorally disruptive effects of the drug, or simple habituation occurs to the drug stimuli. If the contextual stimuli are changed or the task contingencies change, the tolerance may be reduced or eliminated. Pharmacodynamic tolerance refers to changes in cellular membranes, receptors, or neurotransmitter levels reflecting physiological homeostatic processes. These processes are activated when the concentration of the drug is high and the actions are prolonged and are generally independent of the context in which the drug is taken.
Answer to Question 2
If a drug's pharmacodynamic properties result in considerably greater activation of a particular type of receptors (e.g., because the drug is an agonist at the receptors, or the drug causes more than normal amounts of the natural ligand neurotransmitter to be accessible to the receptors) the receptors' functional characteristics may decline (desensitization). Thus, in order to achieve the original effect of the drug, more drug must be taken to act on the remaining receptors that have not desensitized. These receptors will subsequently desensitize, so that even more drug must be taken to produce the original effect. This decrease in the drug's effectiveness results in tolerance.