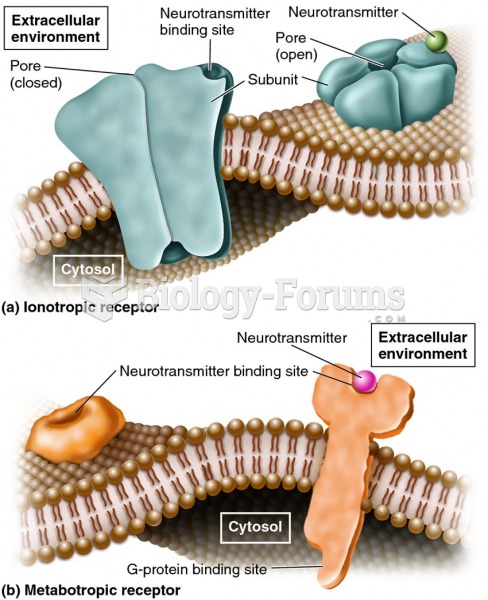
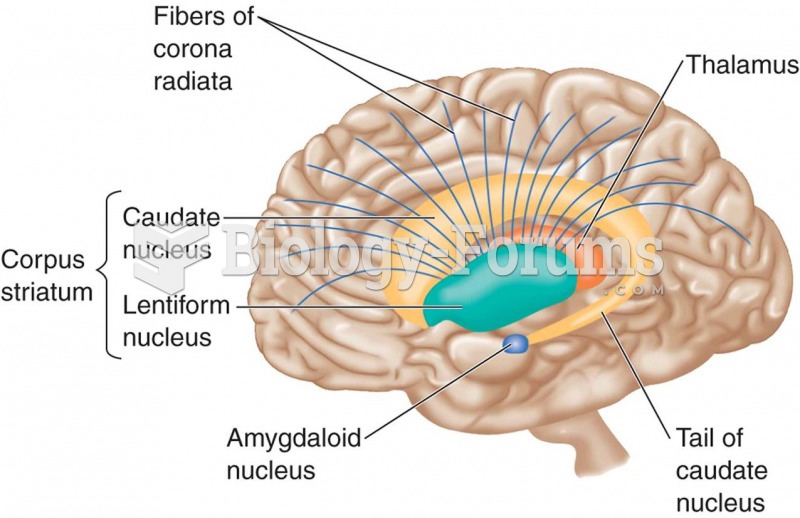
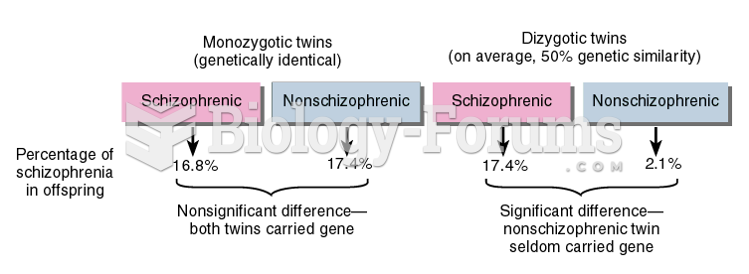
Answer to Question 1
The symptoms of schizophrenia fall into four categories: positive symptoms, negative symptoms, cognitive symptoms and psychomotor abnormalities. Positive symptoms involve unusual thoughts or perceptions such as delusions (false beliefs), hallucinations, disordered thinking (i.e., shifting and unrelated ideas producing incoherent communication), and bizarre behavior. These positive symptoms can be influenced by the individual's mood and can intensity with stress.
Negative symptoms are associated with an inability or decreased ability to initiate actions or speech, express emotions, or feel pleasure. Negative symptoms include avolition (an inability to take action or become goal-oriented), alogia (a lack of meaningful speech), asociality (minimal interest in social relationships), and restricted affect (little or no emotion in situations in which strong reactions are expected).
Cognitive symptoms include problems with attention and memory and difficulty developing a plan of action. Individuals with schizophrenia often have severe to moderately severe cognitive impairments, or poor executive functioning.. This includes deficits in the ability to absorb and interpret information and make decisions based on that information; to sustain attention; and to retain and use recently learned information. Cognitive symptoms are often present before the onset of the first psychotic episode and tend to persist even with treatment.
Psychomotor abnormalities are
extremes in activity level (either unusually high or unusually low), peculiar body movements or postures, strange gestures and grimaces, or a combination of these. People with excited catatonia are agitated and hyperactive. They may talk and shout constantly, moving or running until they drop from exhaustion. They sleep little and are continually on the go.. Their behavior can become dangerous and involve violent acts. In sharp contrast, people experiencing withdrawn catatonia are extremely unresponsive with respect to motor activity. They show prolonged periods of stupor, mutism, and maintain strange postures despite their awareness of all that is going on around them.
Answer to Question 2
c