|
|
|
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women age 65 years of age or older should be screened with bone densitometry.
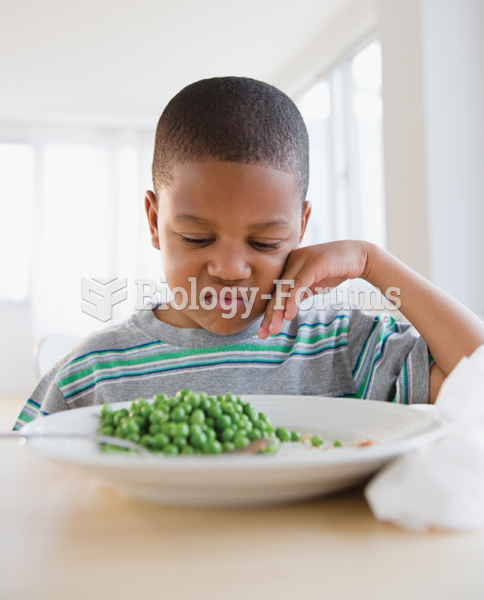
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
Your heart beats over 36 million times a year.
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.