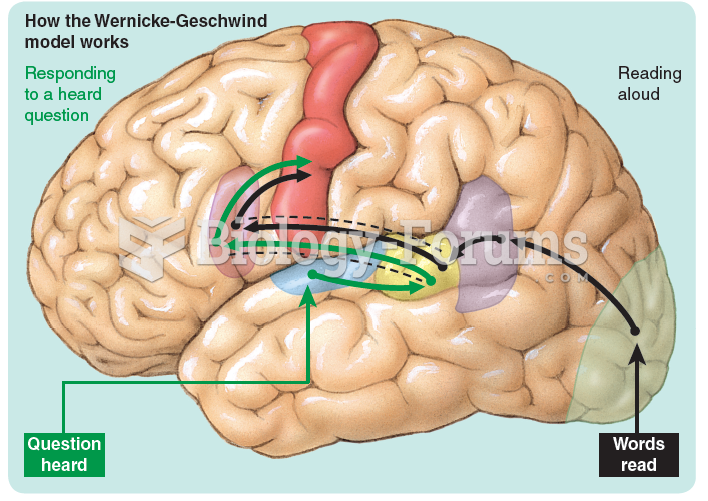
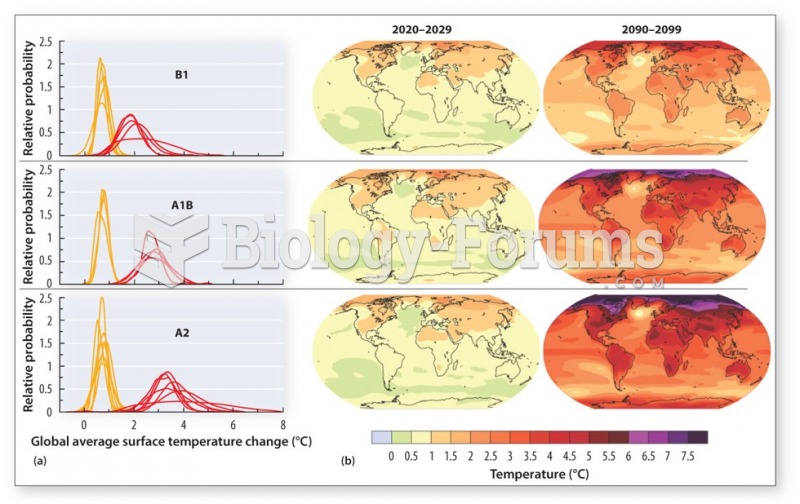
|
|
|
More than 34,000 trademarked medication names and more than 10,000 generic medication names are in use in the United States.
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
In inpatient settings, adverse drug events account for an estimated one in three of all hospital adverse events. They affect approximately 2 million hospital stays every year, and prolong hospital stays by between one and five days.
People often find it difficult to accept the idea that bacteria can be beneficial and improve health. Lactic acid bacteria are good, and when eaten, these bacteria improve health and increase longevity. These bacteria included in foods such as yogurt.
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
 Older adults may grieve intensely over the loss of a person or situation that has been a part of the
Older adults may grieve intensely over the loss of a person or situation that has been a part of the
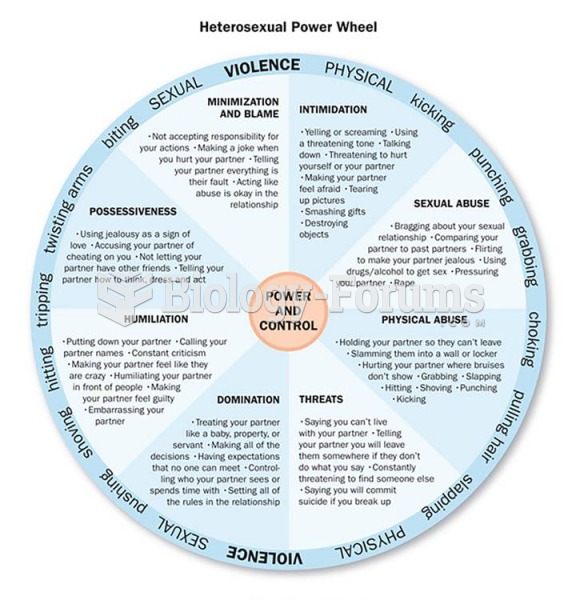 The Power and Control Wheels of Abusive Relationships When one person in a relationship repeatedly ...
The Power and Control Wheels of Abusive Relationships When one person in a relationship repeatedly ...