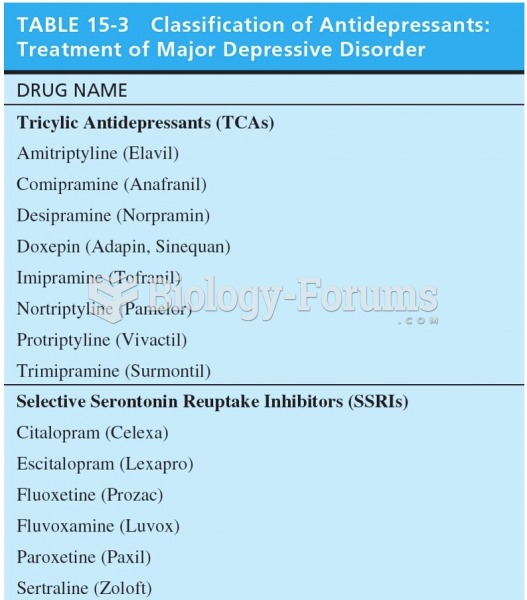
|
|
|
Approximately 15–25% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, many miscarriages often occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
The first-known contraceptive was crocodile dung, used in Egypt in 2000 BC. Condoms were also reportedly used, made of animal bladders or intestines.
 Several species of squirrels have melanistic phases. In large parts of United States and Canada, the
Several species of squirrels have melanistic phases. In large parts of United States and Canada, the
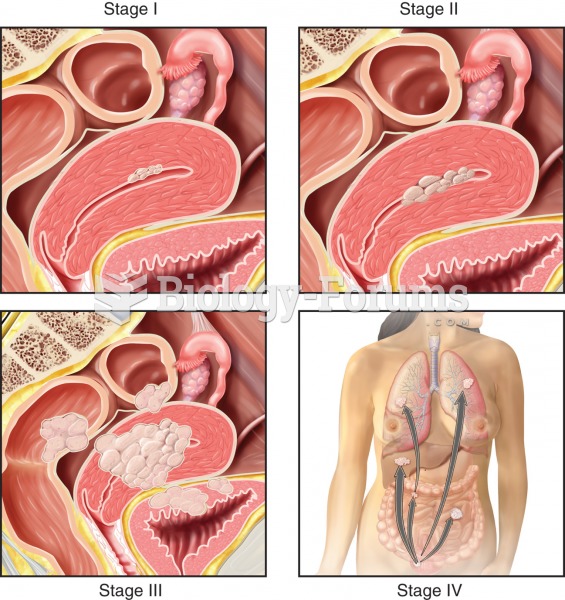 Stages of endometrial cancer. Stage I: Mutated cells arise from glandular epithelium of the endometr
Stages of endometrial cancer. Stage I: Mutated cells arise from glandular epithelium of the endometr
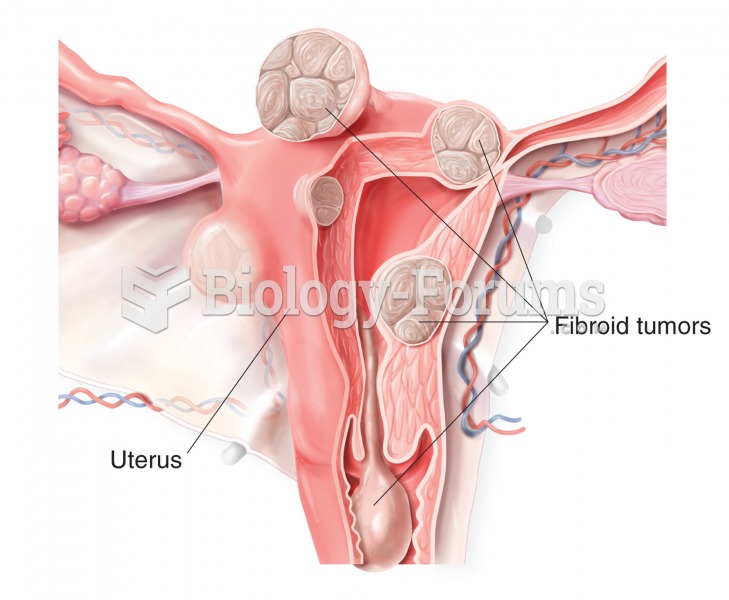 Fibroid tumors, or leiomyomas. Fibroids develop from the uterus to form a variety of hard, round ben
Fibroid tumors, or leiomyomas. Fibroids develop from the uterus to form a variety of hard, round ben