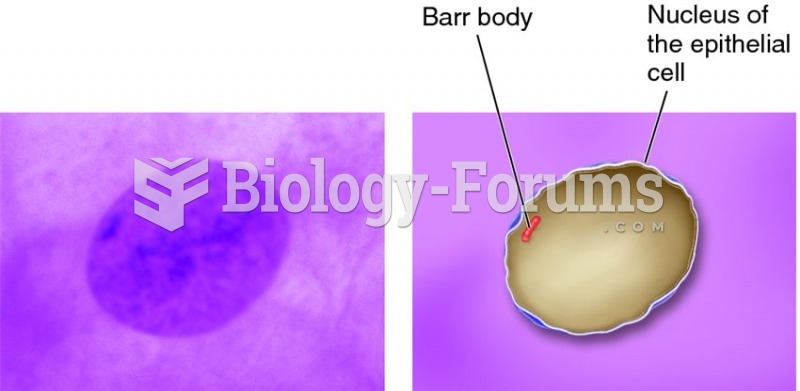
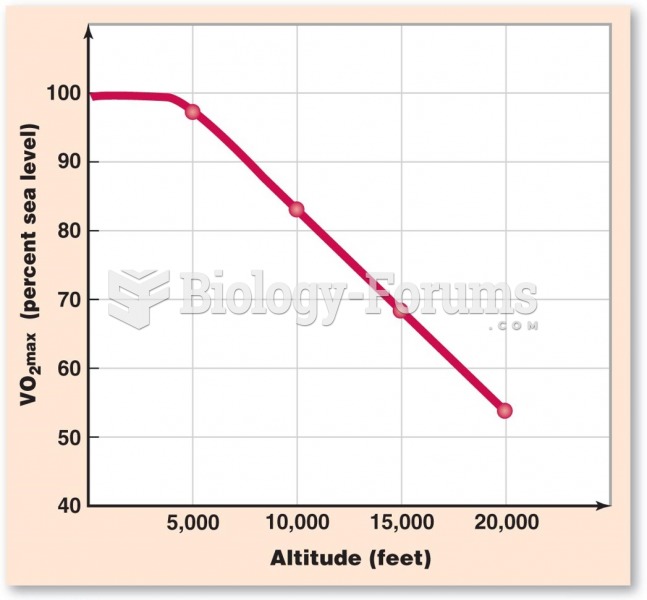
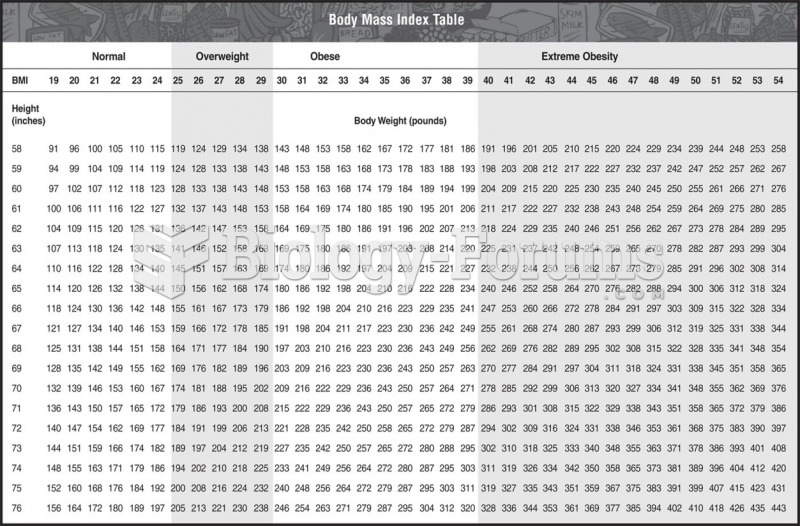
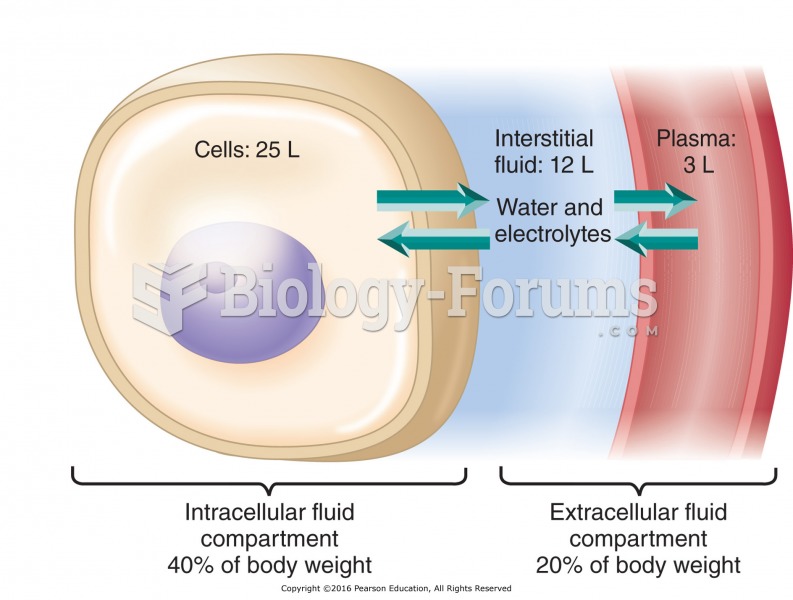
Answer to Question 1
Norepinephrine has much the same effect as epinephrine on the body's systems. However, norepinephrine is released by the adrenal medulla in smaller amounts than epinephrine. The ratio of release is 1 to 5 of norepinephrine to epinephrine though this ratio may change under different conditions. The effects of the circulating hormone norepinephrine last up to 10 times longer than the release of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine on the target cells by the sympathetic post-ganglionic fibers. There is some research to indicate that epinephrine plays a much greater role in mental stressors such as mental arithmetic, and norepinephrine plays a greater role in physical stressors such as physical exercise. Also, epinephrine appears to be most closely associated with the emotional state of fear and norepinephrine with anger. Although both epinephrine and norepinephrine have similar effects on the heart, the effect is greater with epinephrine. Epinephrine also produces 5 to 10 times the acceleration of the body's metabolic rate than norepinephrine and is capable of more than doubling the body's normal rate.
Answer to Question 2
Epinephrine has a marked effect on the cardiovascular system causing both an increase in heart rate and stroke volume as well as constriction of some blood vessels (the arterioles of the skin and abdominal viscera) and dilation of others (the arterioles of the skeletal muscles). The net effect is to shunt blood away from the outer periphery and digestive system and into the brain and large skeletal muscles. It also dilates the bronchi of the lungs to increase oxygen intake into the blood stream. Epinephrine helps to stimulate the release of glucose (i.e., sugar) into the blood stream from glycogen (long chains of glucose) stores in the liver and muscles and through a process called gluconeogenesis converts non-carbohydrate energy stores into glucose for use by the skeletal muscles. The net effect is an increase in the body's metabolic rate (the amount of energy expended by the body). In general, the hormone epinephrine has the same effect as the sympathetic nervous system on its target organs. For example, epinephrine injections given to treat severe allergic reactions can produce sympathetic pattern side effects such as a racing heart, nausea, sweating, tremors, headaches, and feelings of anxiety.