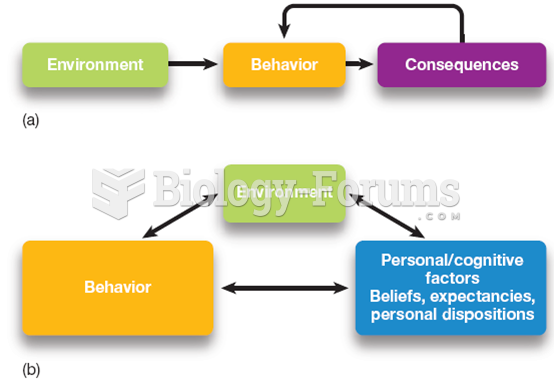
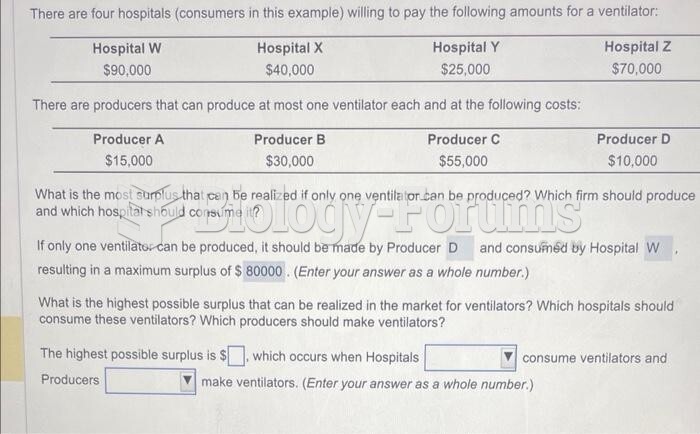
|
|
|
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
In 1864, the first barbiturate (barbituric acid) was synthesized.
In women, pharmacodynamic differences include increased sensitivity to (and increased effectiveness of) beta-blockers, opioids, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and typical antipsychotics.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
Intradermal injections are somewhat difficult to correctly administer because the skin layers are so thin that it is easy to accidentally punch through to the deeper subcutaneous layer.
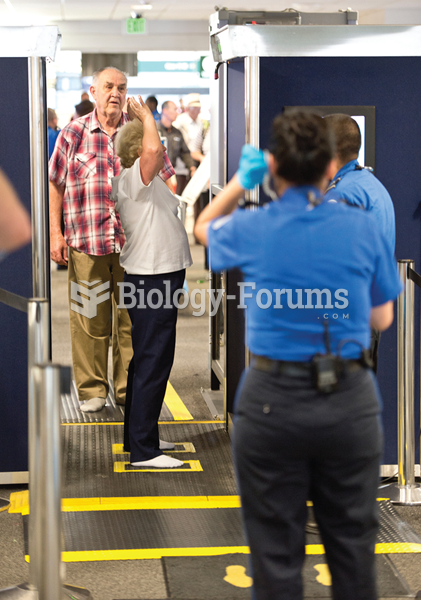 In 2013, Americans learned that the federal government massively surveys their phone calls and e-mai
In 2013, Americans learned that the federal government massively surveys their phone calls and e-mai
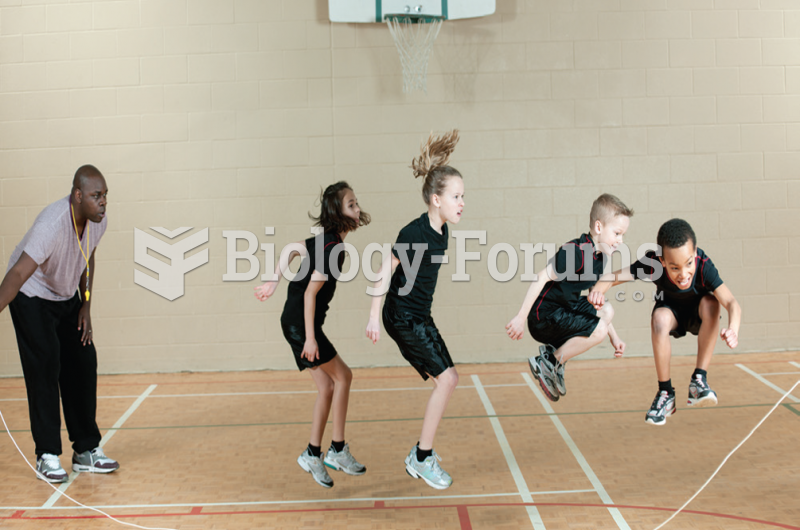
 Shy children often have a high arousal level in novel social situations. Over time, parents can help ...
Shy children often have a high arousal level in novel social situations. Over time, parents can help ...