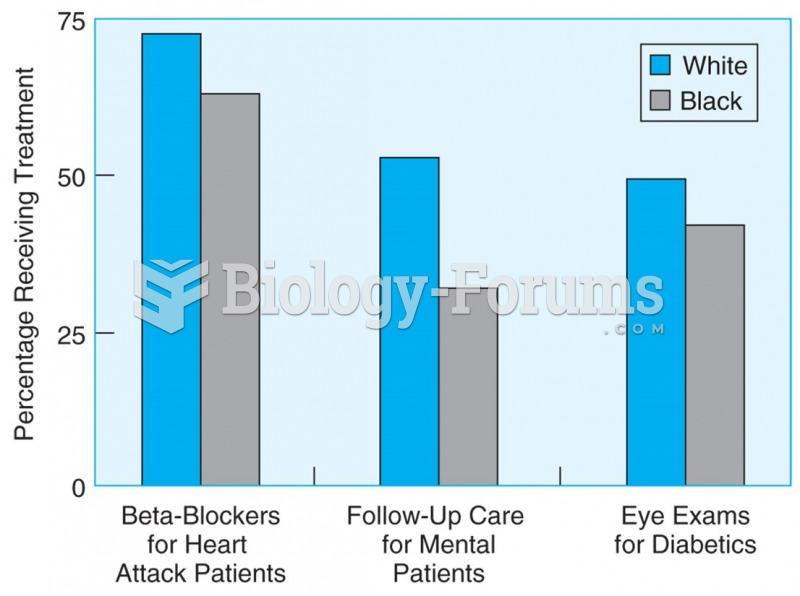
|
|
|
All adults should have their cholesterol levels checked once every 5 years. During 2009–2010, 69.4% of Americans age 20 and older reported having their cholesterol checked within the last five years.
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.
For about 100 years, scientists thought that peptic ulcers were caused by stress, spicy food, and alcohol. Later, researchers added stomach acid to the list of causes and began treating ulcers with antacids. Now it is known that peptic ulcers are predominantly caused by Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped bacterium that normally exist in the stomach.
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.