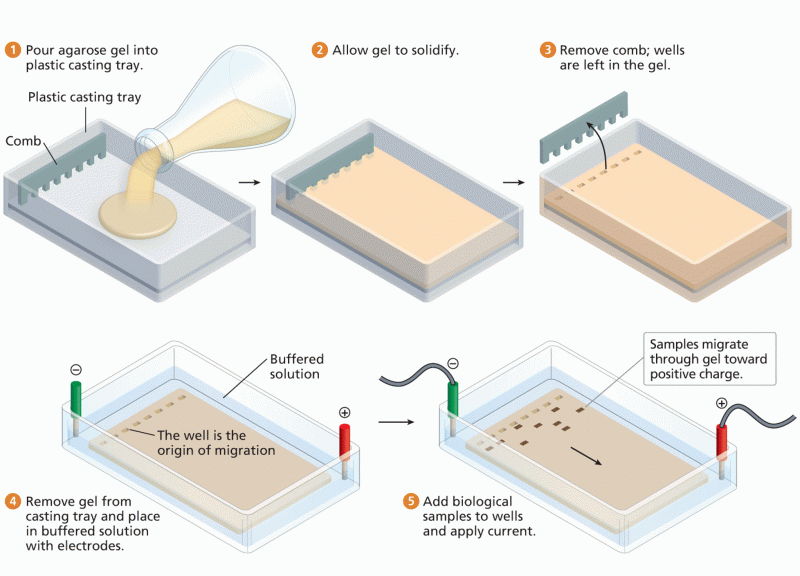
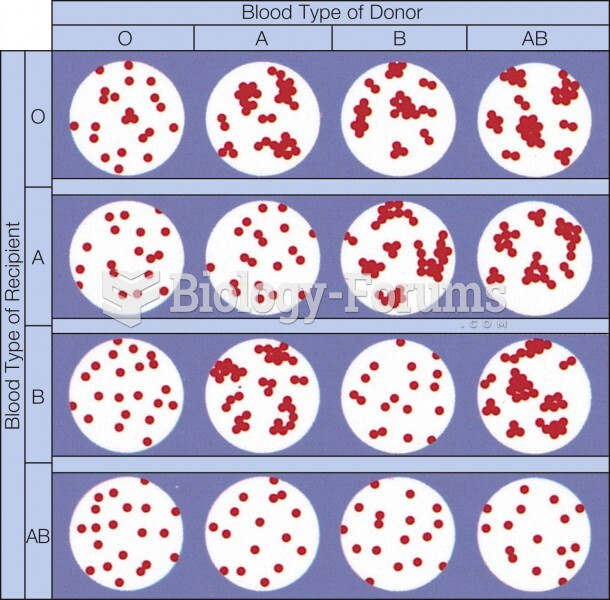
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
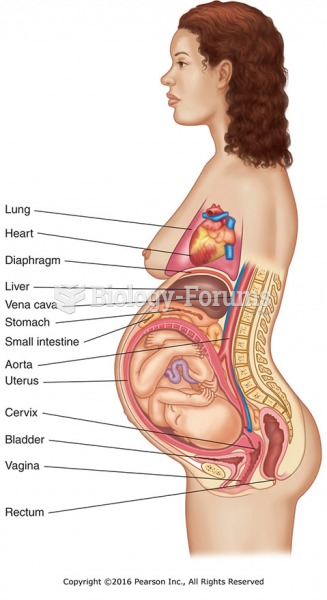
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
Did you know?
According to the FDA, adverse drug events harmed or killed approximately 1,200,000 people in the United States in the year 2015.
Did you know?
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
Did you know?
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Did you know?
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.