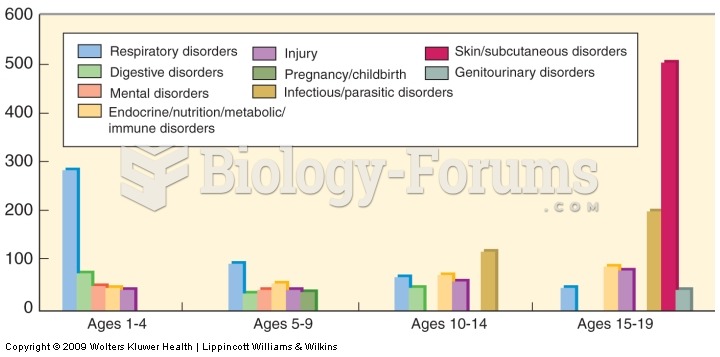
Answer to Question 1
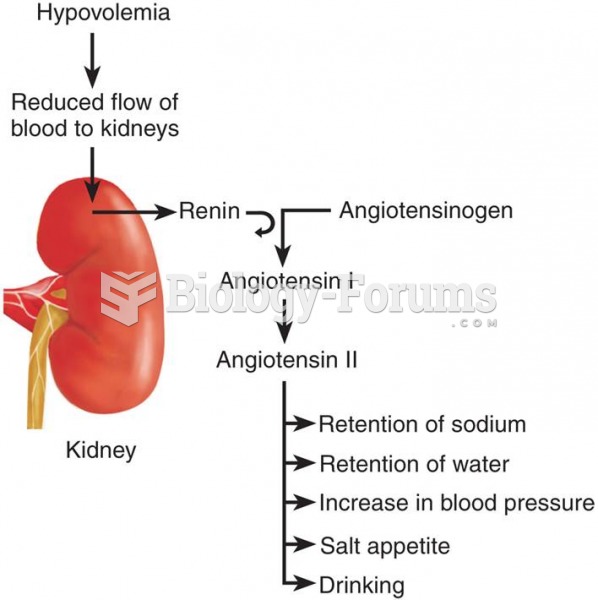
The kidneys maintain homeostatic balance in the body through 3 basic functions:
Filtration: Continuous filtration of blood removes waste products and fluid
Blood pressure control:
Specialized cells (of the glomerulus) in the kidneys secrete renin to form angiotensin I
Angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II, a powerful vasoconstrictor
Angiotensin II also stimulates production of aldosterone and control of blood pressure
Hormone production:
Kidneys produce erythropoietin, a hormone responsible for red blood cell production in bone marrow
Active form of vitamin D is also produced by the kidneys, allowing calcium to be absorbed
Answer to Question 2
Malnutrition associated with chronic disease - this includes chronic diseases or conditions that have sustained mild to moderate inflammation (organ failure, pancreatic cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, chronic kidney disease, etc.)
Loss in lean body mass is gradual and can eventually reach significant depletion over time (several months). With nutritional intervention, lean body mass loss is slowed or potentially reversed.
Positive response to nutrition intervention also requires successful medical treatment of underlying disease.
Malnutrition associated with acute illness and inflammation - this includes acute diseases or injury states with acute and severe inflammatory responses (major infection, burns, trauma, or closed head injury)
Significant depletion of lean body mass occurs over a short period of time (<1 month) without nutritional intervention. there are persistent signs of inflammation. with intervention, lean body mass loss is slowed, but still occurs if inflammation persists.
Priority of nutrition intervention is to provide nutrients to support organ system function and preserve immune function while acute medical treatment is provided.