|
|
|
Less than one of every three adults with high LDL cholesterol has the condition under control. Only 48.1% with the condition are being treated for it.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Risperdal, an adult antipsychotic drug, for the symptomatic treatment of irritability in children and adolescents with autism. The approval is the first for the use of a drug to treat behaviors associated with autism in children. These behaviors are included under the general heading of irritability and include aggression, deliberate self-injury, and temper tantrums.
Sildenafil (Viagra®) has two actions that may be of consequence in patients with heart disease. It can lower the blood pressure, and it can interact with nitrates. It should never be used in patients who are taking nitrates.
Your heart beats over 36 million times a year.
Certain topical medications such as clotrimazole and betamethasone are not approved for use in children younger than 12 years of age. They must be used very cautiously, as directed by a doctor, to treat any child. Children have a much greater response to topical steroid medications.
 Muskox populations remain in the Arctic all year, though they migrate to higher elevations in the wi
Muskox populations remain in the Arctic all year, though they migrate to higher elevations in the wi
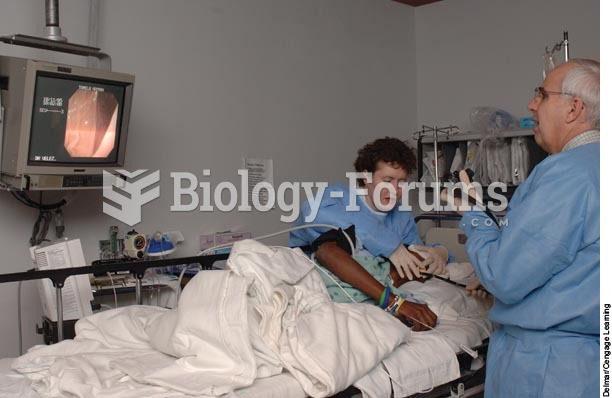 A client is having an endoscopy performed by a physician who views the upper gastrointestinal intern
A client is having an endoscopy performed by a physician who views the upper gastrointestinal intern