|
|
|
Children with strabismus (crossed eyes) can be treated. They are not able to outgrow this condition on their own, but with help, it can be more easily corrected at a younger age. It is important for infants to have eye examinations as early as possible in their development and then another at age 2 years.
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
As the western states of America were settled, pioneers often had to drink rancid water from ponds and other sources. This often resulted in chronic diarrhea, causing many cases of dehydration and death that could have been avoided if clean water had been available.
Symptoms of kidney problems include a loss of appetite, back pain (which may be sudden and intense), chills, abdominal pain, fluid retention, nausea, the urge to urinate, vomiting, and fever.
Nearly 31 million adults in America have a total cholesterol level that is more than 240 mg per dL.
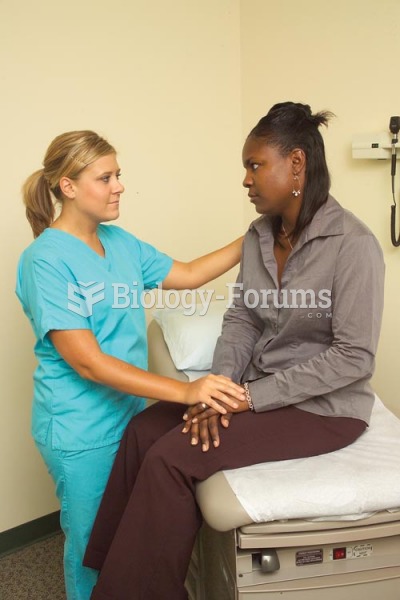 In the communication technique of collaborating, the nurse sends the message that the nurse and pati
In the communication technique of collaborating, the nurse sends the message that the nurse and pati
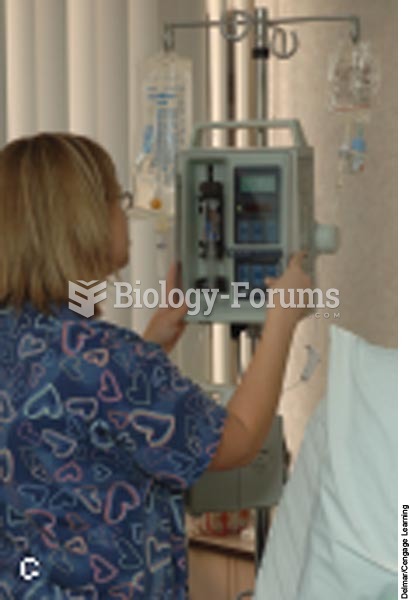 C, A nurse can also administer the medication by setting the dose and rate with an electronic infusi
C, A nurse can also administer the medication by setting the dose and rate with an electronic infusi