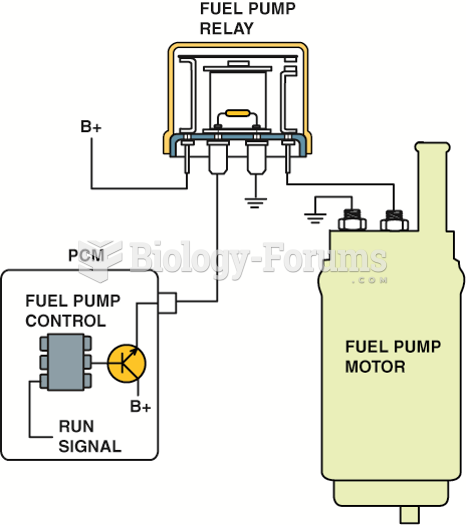
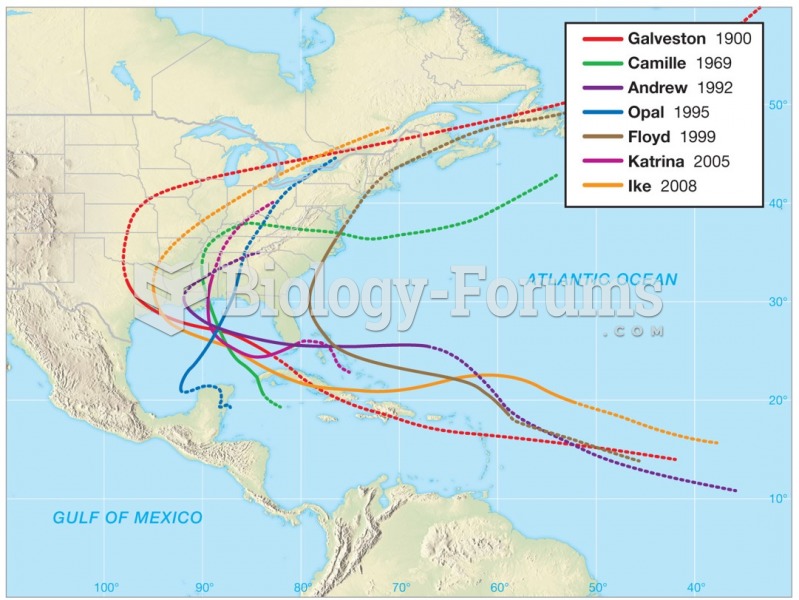
|
|
|
Side effects from substance abuse include nausea, dehydration, reduced productivitiy, and dependence. Though these effects usually worsen over time, the constant need for the substance often overcomes rational thinking.
Symptoms of kidney problems include a loss of appetite, back pain (which may be sudden and intense), chills, abdominal pain, fluid retention, nausea, the urge to urinate, vomiting, and fever.
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
Adult head lice are gray, about ? inch long, and often have a tiny dot on their backs. A female can lay between 50 and 150 eggs within the several weeks that she is alive. They feed on human blood.
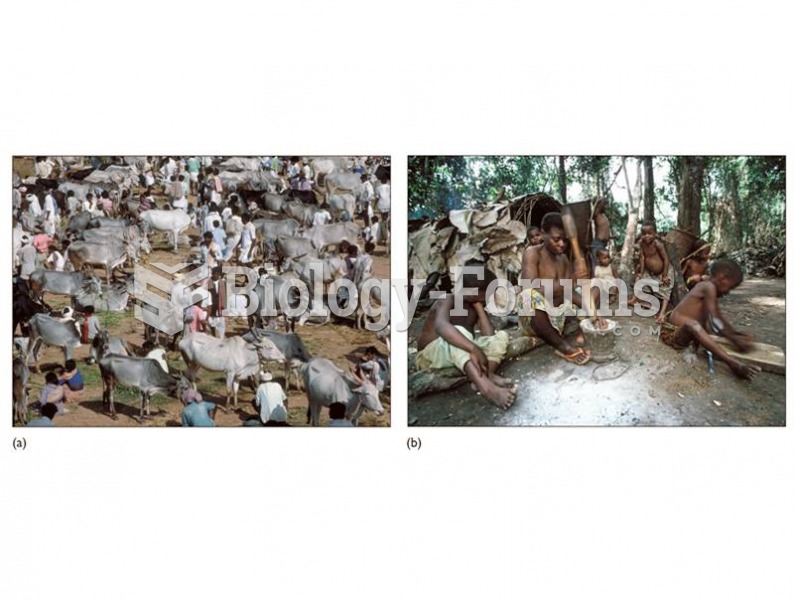 Risks of infectious disease increase in (a) high-density agricultural populations compared to (b) lo
Risks of infectious disease increase in (a) high-density agricultural populations compared to (b) lo
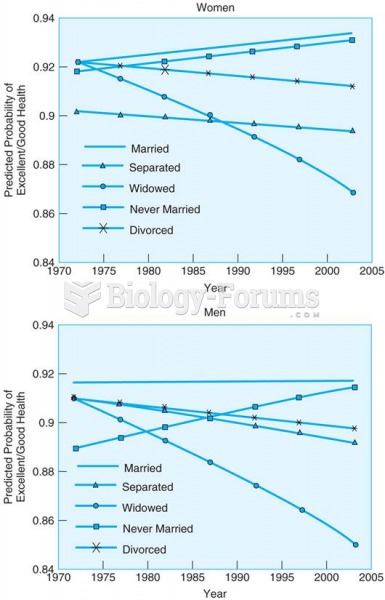 Over the past four decades, the self-reported health of married men and women has remained high, ...
Over the past four decades, the self-reported health of married men and women has remained high, ...