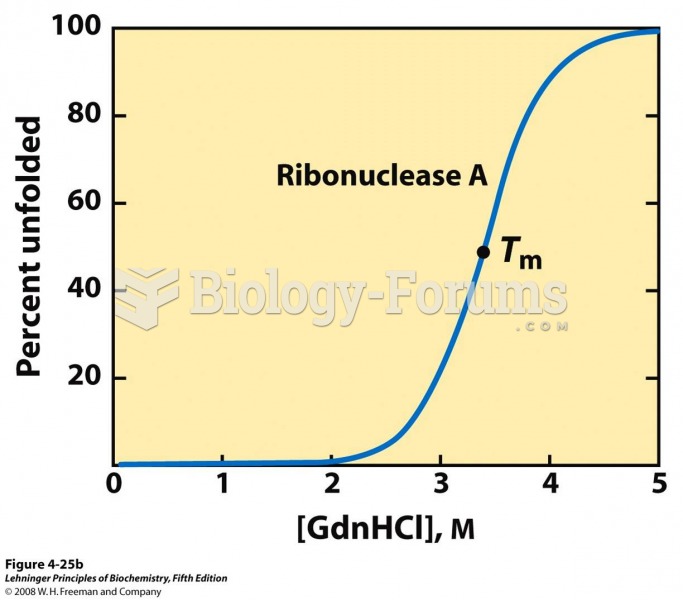
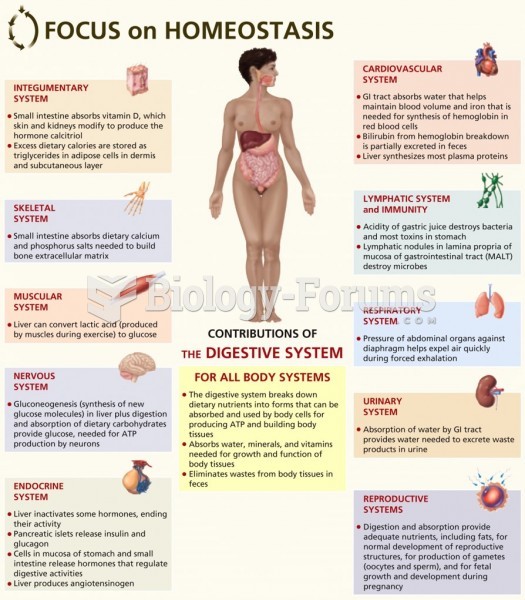
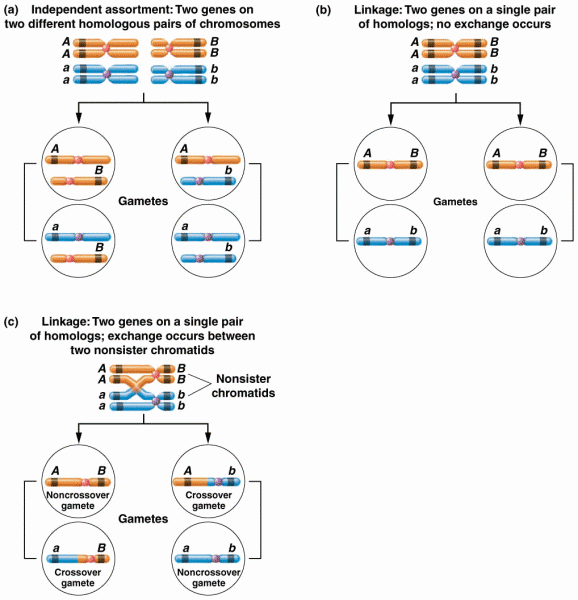
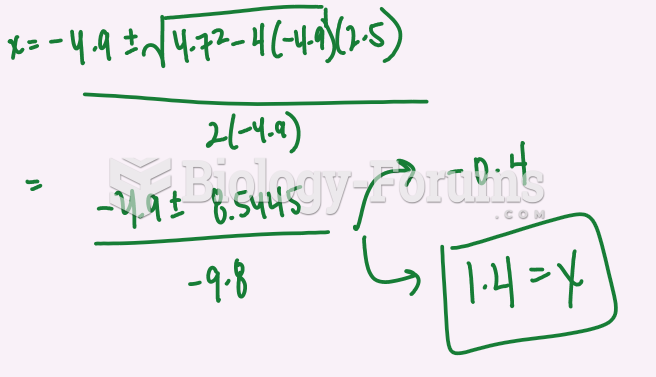This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
Did you know?
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Did you know?
In 1864, the first barbiturate (barbituric acid) was synthesized.
Did you know?
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
Did you know?
The senior population grows every year. Seniors older than 65 years of age now comprise more than 13% of the total population. However, women outlive men. In the 85-and-over age group, there are only 45 men to every 100 women.