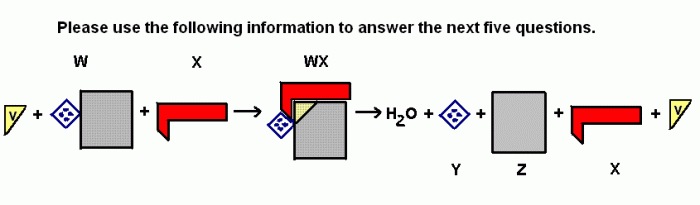
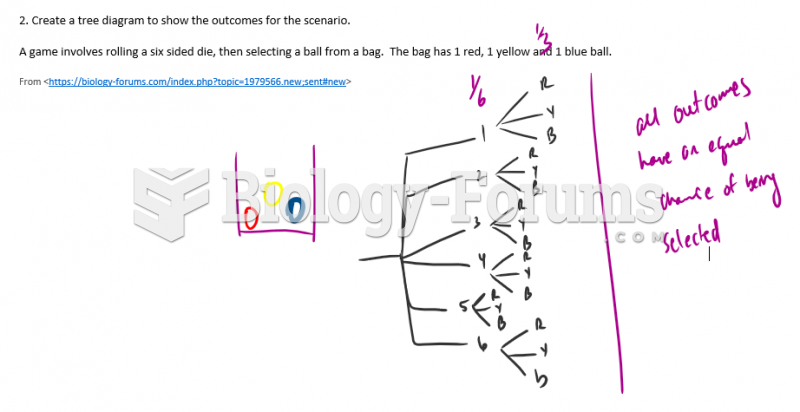
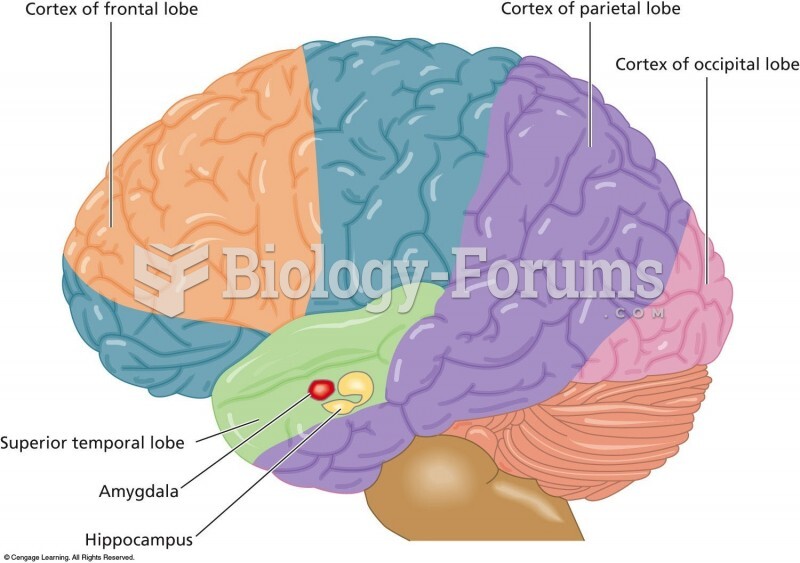
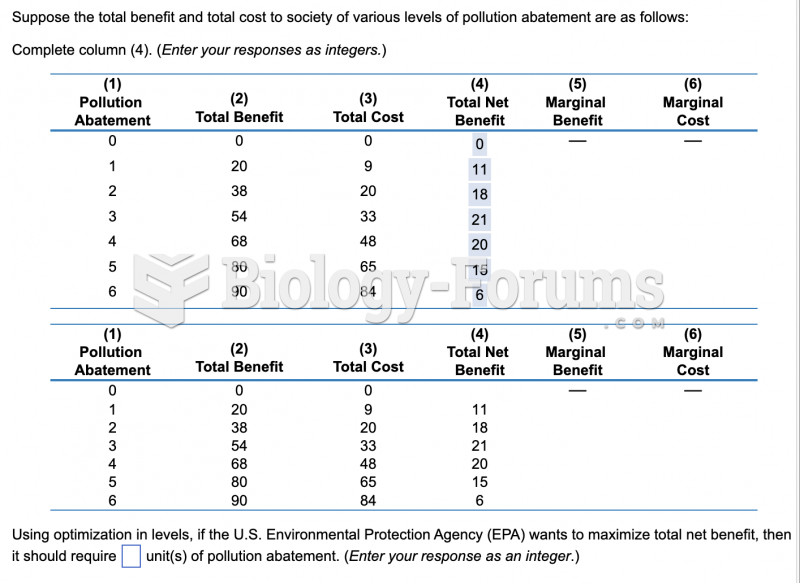
|
|
|
Certain topical medications such as clotrimazole and betamethasone are not approved for use in children younger than 12 years of age. They must be used very cautiously, as directed by a doctor, to treat any child. Children have a much greater response to topical steroid medications.
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
Certain rare plants containing cyanide include apricot pits and a type of potato called cassava. Fortunately, only chronic or massive ingestion of any of these plants can lead to serious poisoning.
Anti-aging claims should not ever be believed. There is no supplement, medication, or any other substance that has been proven to slow or stop the aging process.
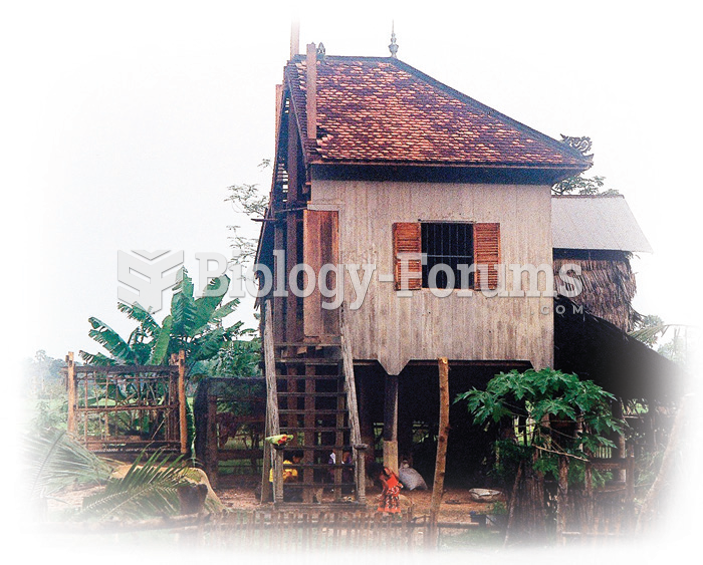 Divorces are often messy. To settle the question of who gets the house, a couple in Cambodia sawed ...
Divorces are often messy. To settle the question of who gets the house, a couple in Cambodia sawed ...
 The study of how traits such as flower color are passed from generation to generation provided the m
The study of how traits such as flower color are passed from generation to generation provided the m