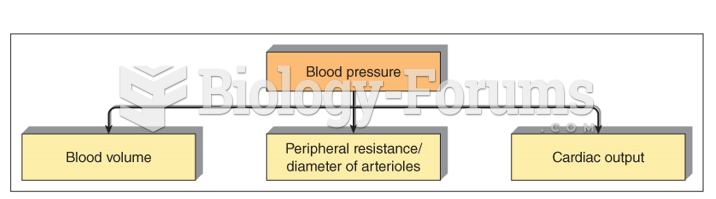
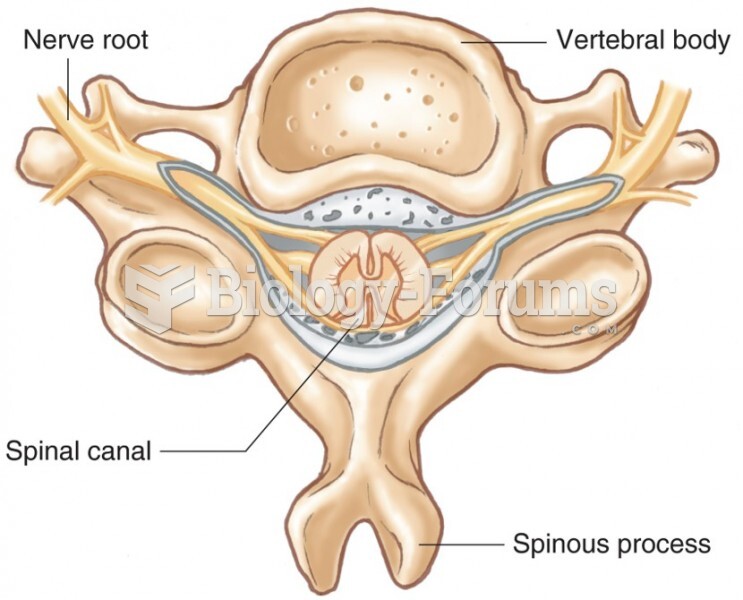
|
|
|
Did you know?
Your chance of developing a kidney stone is 1 in 10. In recent years, approximately 3.7 million people in the United States were diagnosed with a kidney disease.
Did you know?
Only one in 10 cancer deaths is caused by the primary tumor. The vast majority of cancer mortality is caused by cells breaking away from the main tumor and metastasizing to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or liver.
Did you know?
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
Did you know?
This year, an estimated 1.4 million Americans will have a new or recurrent heart attack.
Did you know?
The term pharmacology is derived from the Greek words pharmakon("claim, medicine, poison, or remedy") and logos ("study").
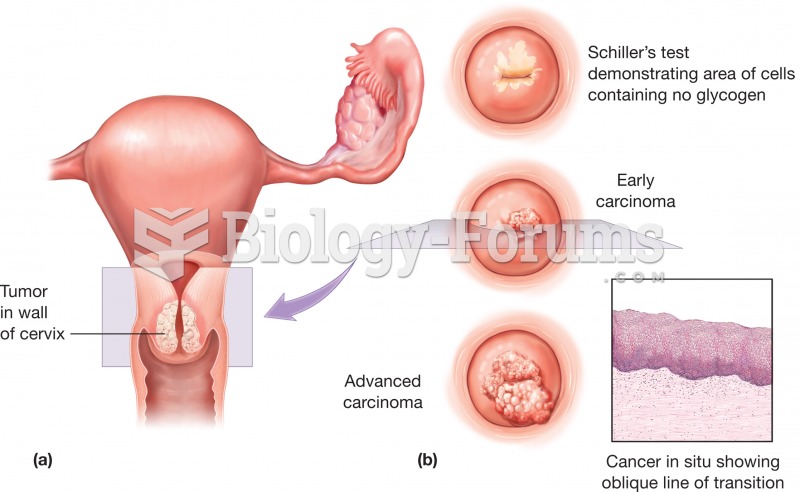 Cervical cancer (a) Top view of the uterus showing the presence of a tumor in the wall of the cervix
Cervical cancer (a) Top view of the uterus showing the presence of a tumor in the wall of the cervix
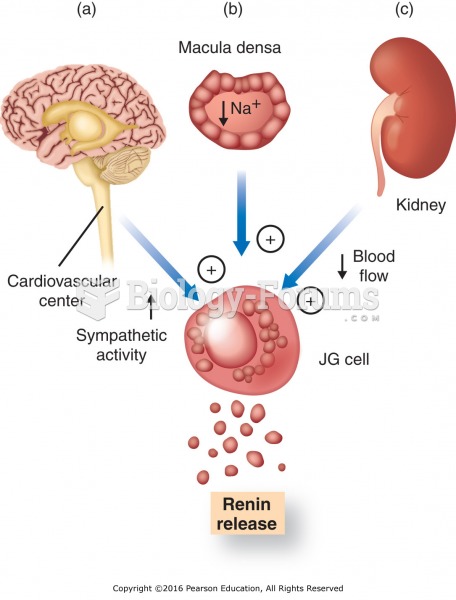 Overview of factors affecting renin release: (a) activation of the sympathetic nervous system; (b) ...
Overview of factors affecting renin release: (a) activation of the sympathetic nervous system; (b) ...