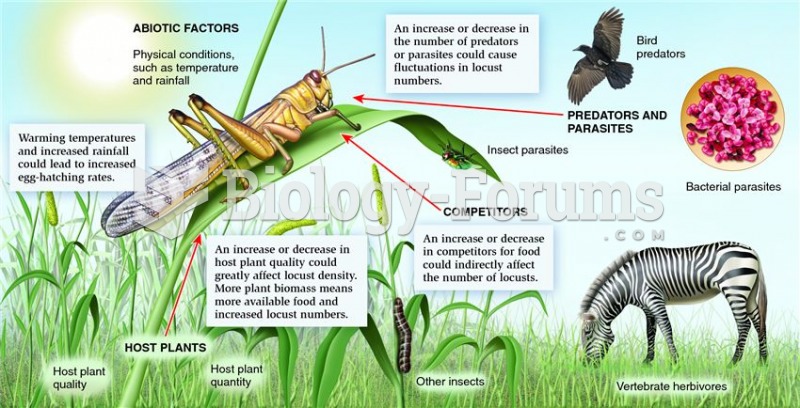
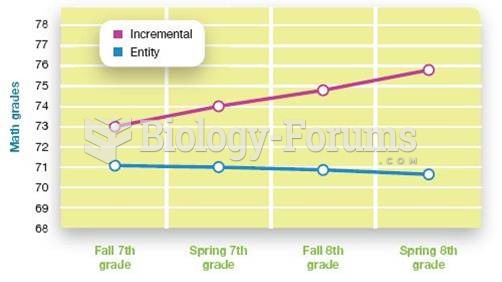
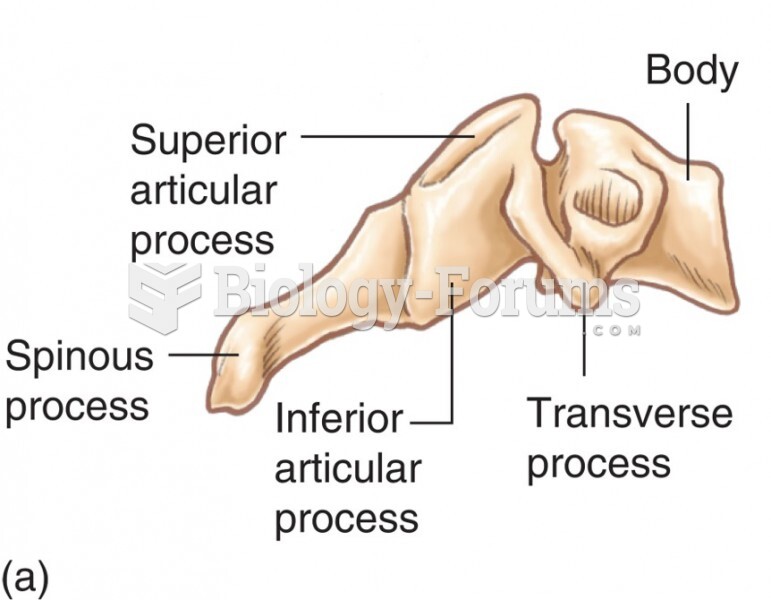
|
|
|
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
Once thought to have neurofibromatosis, Joseph Merrick (also known as "the elephant man") is now, in retrospect, thought by clinical experts to have had Proteus syndrome. This endocrine disease causes continued and abnormal growth of the bones, muscles, skin, and so on and can become completely debilitating with severe deformities occurring anywhere on the body.
During pregnancy, a woman is more likely to experience bleeding gums and nosebleeds caused by hormonal changes that increase blood flow to the mouth and nose.
Human kidneys will clean about 1 million gallons of blood in an average lifetime.
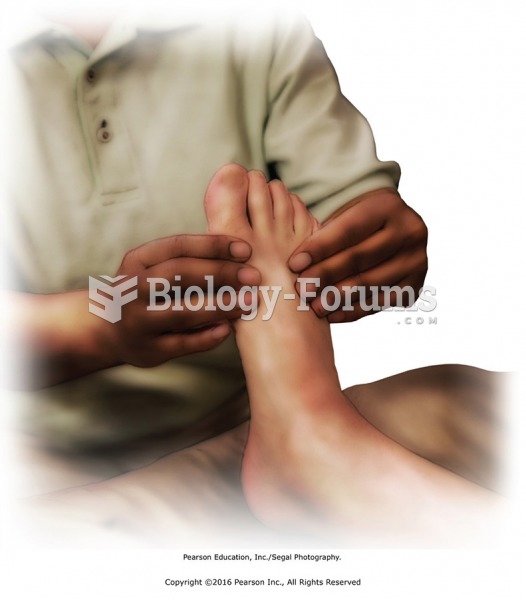
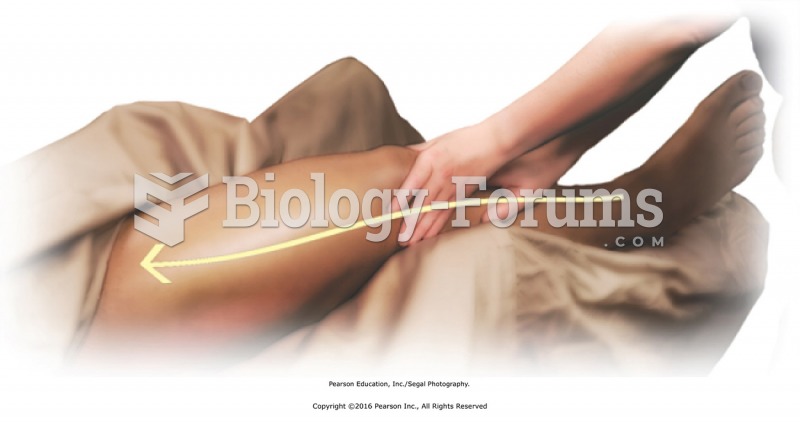 Apply lubricant to the entire right limb using basic sliding effleurage. Apply moderate pressure ...
Apply lubricant to the entire right limb using basic sliding effleurage. Apply moderate pressure ...
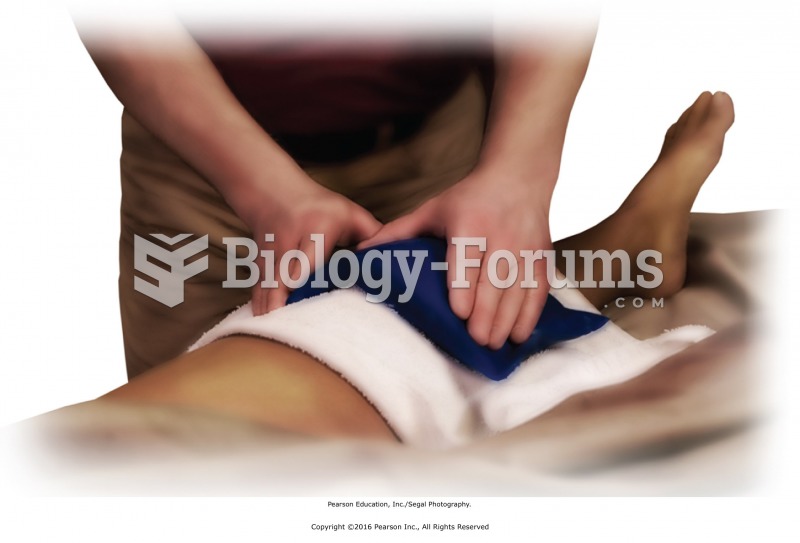 Apply the cold source, and ask for immediate feedback. Conform the cold source to the shape of the ...
Apply the cold source, and ask for immediate feedback. Conform the cold source to the shape of the ...